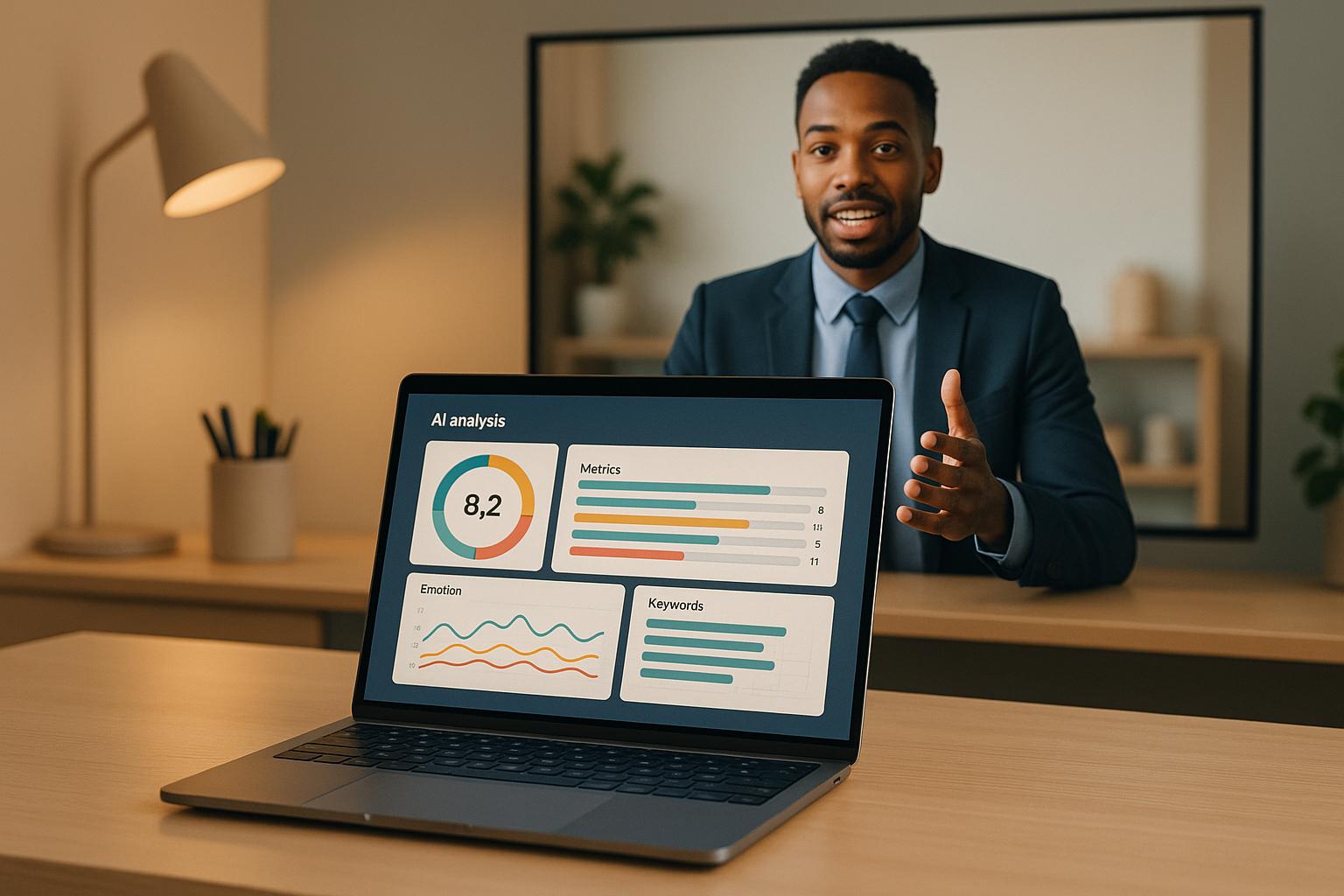
AI is transforming hiring by evaluating video interviews with speed and precision. It examines facial expressions, vocal tones, and speech patterns using advanced tools like computer vision and natural language processing (NLP). The result? Faster, more consistent evaluations that help recruiters identify top candidates, especially in fields like IT and cybersecurity. Here’s what you need to know:
- What It Does: AI analyzes visual cues, tone, and language in video interviews, whether live or recorded.
- Why It’s Useful: Speeds up hiring, reduces bias, and ensures consistent scoring across candidates.
- How It Works: Processes video and audio data, converts speech to text, and scores candidates based on job-specific criteria.
- Challenges: AI may struggle with nuanced responses or diverse accents and requires ethical oversight to avoid bias.
AI is best used as a tool to support human decision-making, not replace it. Combining AI’s efficiency with human judgment creates a balanced, fair hiring process.
How to Ace an AI Video Interview | #Hirevue
Data Preparation for AI Analysis
Getting data ready and properly formatted is a crucial first step for accurate AI analysis. When it comes to video interview analysis, thorough preparation ensures AI can operate at its best.
This process involves turning raw video recordings into a structured format. Each step needs close attention – mistakes early on can ripple through and impact the entire analysis.
Collecting and Formatting Video Data
Start by capturing video interviews in widely used formats like MP4 or AVI, which are compatible with most processing tools. The recording setup is key: videos should have a high resolution and frame rate to clearly capture facial expressions and body language. Audio quality must also be top-notch, with minimal background noise or distractions.
Organizing files with consistent naming conventions – such as including the candidate ID, interview date, and job role – makes managing large volumes of video easier. Storing these files in a robust cloud system ensures they’re secure and accessible, while sufficient bandwidth supports smooth workflows for AI processing.
To manage storage costs without compromising analysis quality, video compression is essential. Encoding methods like H.264 strike a balance between reducing file sizes and maintaining visual clarity.
Ensuring Data Quality for Analysis
Good quality video and audio are non-negotiable for accurate AI analysis. Clear audio is especially critical, as background noise, echoes, or poor microphone quality can disrupt speech recognition. Setting up interviews in a quiet space and testing audio equipment beforehand can help avoid these issues.
Lighting also plays a big role. Well-lit environments, whether using natural light or soft LED panels, make it easier for AI to detect facial details and subtle expressions. Keeping the camera stable and fixed prevents unnecessary movement, ensuring smooth analysis of body language.
Data validation checks are another safeguard. Automated systems can flag issues like low audio levels, poor lighting, or technical glitches, allowing you to fix problems before analysis begins. Standardizing interview formats further ensures consistency, making it easier to compare candidates’ responses.
Speech-to-Text Conversion
Converting speech to text is a critical step for analyzing language and sentiment. Modern speech-to-text systems are highly accurate when conditions are ideal, but performance can drop with poor audio quality or strong accents. Factors like processing power and the complexity of the audio also influence results.
Specialized terms, such as "Kubernetes", "OAuth", or "SIEM platforms", can be tricky for standard systems to handle. Incorporating industry-specific dictionaries into advanced systems improves recognition of these terms, ensuring technical language is captured correctly.
For interviews with multiple speakers, distinguishing between the interviewer and the candidate is essential. AI systems use speaker identification and timestamps to link text to specific moments in the video. This allows for a deeper analysis that combines verbal responses with nonverbal cues.
After transcription, error correction algorithms clean up the text by removing filler words and false starts. The result is a polished transcript that reflects the candidate’s communication style and technical knowledge. This transcript serves as the foundation for advanced AI analyses, such as evaluating facial expressions, tone, and sentiment.
Core AI Techniques in Video Interview Analysis
AI brings a new dimension to candidate evaluation by focusing on non-verbal cues. One standout approach is the analysis of body language and gestures, offering insights that traditional methods might overlook. These cues play a crucial role in understanding a candidate’s behavior and communication style.
Body Language and Gesture Detection
By combining computer vision, deep learning, and behavioral science, AI systems can analyze facial expressions and gestures captured in real-time video. These technologies work together to decode subtle movements and expressions, providing a deeper understanding of a candidate’s demeanor.
sbb-itb-05efa2a
AI Scoring and Evaluation Processes
Once high-quality video and accurate transcripts are ready, AI takes over to transform interview data into measurable scores.
Automated Scoring Systems
After preparing the data, AI evaluates performance using structured scoring methods tailored to specific job roles. These systems rely on weighted criteria to assess candidates.
Here’s how it works: AI examines technical skills by recognizing keywords and assessing response accuracy. It evaluates communication skills by analyzing speech clarity and the structure of responses. For cultural alignment, AI uses sentiment analysis and behavioral pattern recognition to gauge fit.
Each area is scored on a 0–100 scale. These scores are then combined using pre-set weightings to produce an overall rating. For example, in a software engineering role, technical skills might account for 40% of the score, while communication and problem-solving each contribute 30%.
AI also factors in confidence levels for its assessments. If audio quality is poor or responses are ambiguous, the system assigns lower confidence scores, flagging these for human review.
Key Topic Identification
AI doesn’t just score – it also highlights the main themes of an interview, giving recruiters a quick snapshot of a candidate’s focus on important topics.
Using natural language processing (NLP), AI scans transcripts to find recurring themes, technical terms, and clusters of related concepts. Beyond just identifying topics, it uncovers communication patterns that might escape human notice. For instance, it can detect if a candidate frequently revisits certain subjects, avoids others, or shows varying enthusiasm for different aspects of the role.
To make this even clearer, AI generates topic heat maps – visual tools that show how much time and attention candidates spend on various subjects. These maps help hiring managers pinpoint candidates who naturally emphasize key aspects of the job versus those who dwell on less relevant topics. This added layer of analysis sharpens the evaluation process, offering a balanced view of strengths and areas for improvement.
Pros and Cons of AI Scoring
AI scoring systems come with a mix of benefits and challenges. Understanding both sides helps organizations decide how to best integrate this technology into their hiring processes.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Ensures consistent evaluation criteria for all candidates, eliminating human judgment inconsistencies | Lacks contextual understanding, which might overlook nuanced or creative responses |
| Processes large volumes of candidates quickly, cutting hiring timelines from weeks to days | Risks algorithmic bias if training data lacks diversity or has inherent flaws |
| Offers objective scoring based on defined metrics, reducing subjectivity | Relies on technology, requiring stable internet, good-quality video/audio, and candidate comfort with digital tools |
| Provides detailed documentation for compliance and feedback purposes | May result in a weaker human connection, potentially affecting the candidate experience and employer branding |
| Operates 24/7, allowing candidates to complete interviews at their convenience | Struggles with assessing soft skills like empathy, creativity, or leadership, which often need human interpretation |
The effectiveness of AI scoring depends heavily on how well it’s implemented and maintained. Companies that use AI as a complementary tool – rather than a replacement for human judgment – tend to see better results. Regular audits and bias testing are crucial to ensure the system remains accurate and fair across diverse candidate pools.
A hybrid approach often works best. AI can handle initial screening and data analysis, while human recruiters focus on final evaluations and building relationships with candidates. This balance combines the efficiency of AI with the nuanced insights only humans can provide.
Implementing AI Video Analysis in Recruitment Workflows
To effectively implement AI video analysis in hiring, organizations need a well-thought-out strategy that prioritizes human oversight and ethical considerations. Building on earlier discussions about data preparation and scoring, the focus shifts to streamlining recruitment processes.
Integrating AI into Existing Hiring Workflows
The key to successfully introducing AI into hiring is starting small. Instead of overhauling the entire system, organizations should integrate AI into specific stages of the recruitment process, refining it step by step.
For example, companies like Equifier, which specialize in IT staffing and cybersecurity recruitment, can use AI video analysis to screen technical candidates. This technology is particularly useful during the initial stages, where it can identify references to technical skills and specialized knowledge. This allows human recruiters to shift their focus to assessing interpersonal dynamics and conducting in-depth technical interviews in later stages.
A phased rollout is often the most practical approach. Initially, AI can handle tasks like processing large volumes of applications and screening for basic qualifications. Over time, its role can expand to evaluating communication skills, technical expertise, and integrating seamlessly with applicant tracking systems (ATS) and recruiter dashboards.
To make the most of AI, recruiters need proper training to interpret AI-generated scores, confidence levels, and recommendations. They should also feel empowered to override AI decisions when necessary. While there might be some initial skepticism, many recruiters find that the technology reduces repetitive tasks and helps uncover qualified candidates who might otherwise be missed.
From a technical standpoint, organizations need reliable video hosting platforms, sufficient bandwidth for processing, and smooth integration with existing HR systems. Once these systems are in place, attention can turn to addressing ethical and legal considerations.
Ethical Considerations and Bias Mitigation
After integrating AI into recruitment workflows, organizations must address ethical concerns, particularly algorithmic bias. Regular audits and diverse training data are essential to ensure fairness.
Data privacy is another critical issue. Candidates may feel uneasy knowing their facial expressions, tone, and body language are being analyzed. Clear communication about what data is collected, how it’s used, and how long it will be retained can help build trust.
To mitigate bias, organizations should work closely with AI vendors to ensure training data includes diverse representation across race, gender, age, and other demographics. Frequent audits can further ensure that AI scoring doesn’t unfairly disadvantage any group.
A hybrid decision-making model – combining AI insights with human judgment – helps maintain fairness. Additionally, obtaining candidate consent and being transparent about how AI is used in the evaluation process supports more ethical hiring practices.
Ensuring Compliance with Legal Standards
Once ethical concerns are addressed, organizations must ensure compliance with legal standards. Federal guidelines, like those from the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), require that AI tools avoid creating unequal outcomes for protected groups.
State and local laws are also evolving. In some areas, employers are now required to conduct regular bias audits for automated hiring tools and inform candidates when such tools are being used.
Maintaining thorough documentation of AI decision-making processes is essential. This includes keeping records of algorithm versions, confidence scores, and instances of human intervention. Data retention policies should balance privacy with legal obligations, ensuring that video interviews and AI analysis results are stored only as long as necessary.
Accessibility is another key consideration. Under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), employers must provide alternative assessment methods for candidates unable to participate in standard video interviews.
For global organizations, compliance with international regulations like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is crucial. GDPR imposes stricter requirements for consent and data processing than U.S. laws. Regular reviews of AI hiring practices, ideally with input from employment law experts, can help ensure compliance with both domestic and international standards.
Conclusion: The Future of AI in Video Interviews
AI video analysis is reshaping how talent is evaluated, offering insights that traditional interviews often overlook. By analyzing facial expressions, vocal tones, and body language, this technology uncovers layers of information that can enrich the recruitment process.
One of its standout benefits is the combination of efficiency and consistency. Unlike human evaluations, which can vary based on subjective factors, AI provides uniform assessments across countless interviews. This consistency is especially valuable for organizations managing large-scale hiring, where reviewing every interview manually would be overwhelming.
In specialized fields like IT and cybersecurity, AI brings even more to the table. It can pick up on technical language, gauge how clearly candidates explain complex ideas, and even assess confidence during technical discussions. Platforms like Equifier use these capabilities to pinpoint top talent in these industries, ensuring high standards are met without sacrificing speed.
A hybrid approach to recruitment seems to strike the right balance. AI can handle the initial screening – highlighting standout candidates and flagging potential concerns – while recruiters focus on deeper evaluations. This gives recruiters more time for activities like detailed technical interviews and assessing how well candidates might align with a team’s dynamics.
As the technology evolves, it’s likely to become even better at recognizing specific industry skills and problem-solving abilities. However, the human touch will always be essential for evaluating qualities like creativity, leadership, and those intangible traits that define exceptional hires.
Organizations that integrate AI video analysis thoughtfully – ensuring ethical practices and maintaining human oversight – can streamline hiring while still making well-rounded decisions. The goal isn’t full automation but rather using AI to complement human expertise, creating a hiring process that’s both efficient and fair.
FAQs
How does AI promote fairness and reduce bias in video interview evaluations?
AI helps create a more level playing field in video interview evaluations by standardizing both the questions asked and the criteria used for assessment. This ensures every candidate is evaluated under identical conditions, reducing the influence of human bias in hiring decisions.
To take this a step further, AI systems are developed using diverse, representative datasets and are equipped with tools to detect and address potential biases. These efforts are aimed at identifying and correcting any algorithmic issues, making the evaluation process fairer and more inclusive for all applicants.
How can companies ensure ethical use of AI in recruitment?
Companies aiming to use AI ethically in recruitment need to focus on reducing bias by ensuring their training datasets are diverse and representative. This helps create a more balanced system that doesn’t unfairly favor certain groups. Along with this, being transparent about how AI makes its decisions is crucial for building trust with job candidates.
Conducting regular bias audits is another key step. These audits can uncover and address potential fairness concerns, ensuring the hiring process remains equitable. At the same time, protecting candidate privacy is essential – not just for ethical reasons but also to comply with data protection regulations. Lastly, keeping human oversight as part of the process is vital. This ensures that empathy and fairness are central to critical hiring decisions, creating a more inclusive experience for everyone involved.
How does AI manage different accents and technical terms during video interviews?
AI addresses the complexities of diverse accents by training on vast datasets that represent a wide range of speech patterns and dialects. This broad exposure enables it to recognize and interpret different ways of speaking more effectively. When it comes to technical terms, AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand industry-specific jargon within the context of a conversation, ensuring precise interpretation.
Moreover, modern AI systems are designed with bias reduction techniques to limit inaccuracies when processing accents or specialized language. These advancements contribute to a more inclusive and equitable evaluation process, particularly in video interviews.