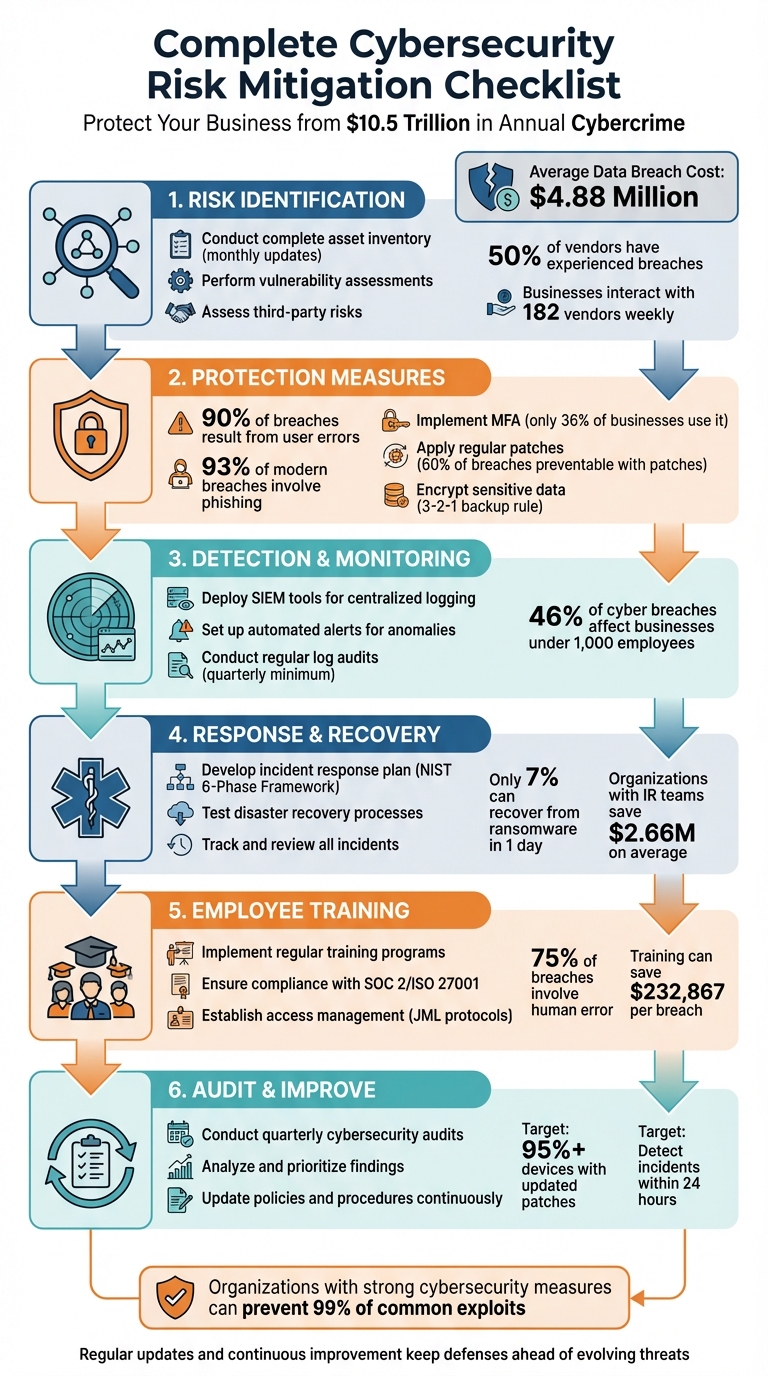
Cybersecurity is a growing concern, with cybercrime projected to cost the global economy $10.5 trillion annually. Businesses of all sizes need to act now to protect their operations, customer trust, and reputation. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help you manage and reduce cybersecurity risks effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Identify Risks: Conduct asset inventories, vulnerability assessments, and evaluate third-party risks.
- Protect Systems: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), apply regular patches, and encrypt sensitive data.
- Monitor Threats: Deploy tools like SIEM for centralized threat detection and set up alerts for anomalies.
- Respond and Recover: Develop and test incident response plans to minimize downtime and costs.
- Train Employees: Regular training can prevent 75% of breaches caused by human error.
- Audit and Improve: Perform quarterly audits to keep defenses updated and address vulnerabilities.
Why It Matters: The average cost of a data breach is $4.88 million, and businesses with strong cybersecurity measures can save millions by preventing attacks. This checklist breaks down the process into manageable steps to help you stay ahead of evolving threats.
6-Step Cybersecurity Risk Mitigation Framework for Businesses
How to Perform a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment (Template Checklist)
sbb-itb-05efa2a
Risk Identification Checklist
Before setting up any security measures, it’s essential to understand your digital environment. This means pinpointing assets, identifying vulnerabilities, and mapping out all external connection points.
"You can’t protect against what you don’t know about. An assessment shines a light on vulnerabilities you may have missed, like unpatched software or misconfigured firewalls, so you can remediate them before attackers strike." – Michael Hendricks, Head of IT Content, Rippling
With the average cost of a data breach hitting $4.88 million, many incidents stem from overlooked systems or unchecked vendor connections. Risk identification isn’t a one-time task – it’s an ongoing process that needs consistent updates. This checklist will walk you through the key steps.
Conduct Complete Asset Inventory
Start by cataloging everything connected to your network. This includes servers, endpoints, cloud resources, and operational technology (OT) devices – essentially, anything with an IP address. During this process, many organizations stumble upon "shadow IT", where unauthorized hardware or software has been added without approval.
Your inventory should be more than just a list. Document baseline configurations for critical devices, and keep network topology maps up to date. Additionally, classify your data based on sensitivity, with special attention to customer information, financial records, and intellectual property – these are frequent targets for attackers. Update this inventory monthly and require formal approval for any new installations.
Perform Vulnerability Assessments
Once your assets are identified, the next step is to figure out where they might be at risk. Automated scanners can help detect common issues like unpatched software, misconfigured settings, or open ports.
However, automated tools alone aren’t enough. Pair them with penetration testing to uncover deeper vulnerabilities. When weaknesses are found, use a risk matrix (likelihood × impact) to prioritize fixes. Organizations with trained incident response teams can significantly cut breach costs – by as much as $2.66 million on average.
Assess Third-Party Risks
Third-party vendors pose a major risk. Over 50% of vendors have experienced breaches, and 73% of businesses report disruptions due to vendor issues. On average, businesses interact with 182 vendors each week.
Classify your vendors based on the sensitivity of the data they handle and the importance of their services. Before onboarding, use security questionnaires to evaluate their technical controls and ensure contracts include clear cybersecurity requirements, like specific timelines for incident notifications. Don’t forget about fourth-party risks, such as subcontractors working with your vendors. Equifier’s cybersecurity consulting services can assist in identifying and addressing these external vulnerabilities before they become a problem.
Once you’ve identified the risks, the next step is to implement safeguards to secure your digital environment.
Protection Measures Checklist
Once you’ve identified risks, the next step is implementing technical safeguards to protect your data.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
Surprisingly, only 36% of businesses use MFA for internal access, and nearly 50% of high-privilege accounts lack it. Considering that 90% of breaches result from user errors, MFA is a must – especially for administrative and privileged accounts.
"Any form of MFA is better than no MFA. Any form of MFA (like SMS text messages, or authenticator codes) will raise the cost of attack and will reduce your risk." – CISA
However, not all MFA methods are created equal. Since 93% of modern data breaches involve phishing attacks, it’s critical to move beyond SMS and push notifications. Instead, adopt phishing-resistant options like FIDO security keys or authenticator apps with number matching. Additionally, disable legacy protocols to minimize vulnerabilities.
| MFA Method | Security Level | Resistance to Phishing |
|---|---|---|
| FIDO / Security Keys | Highest | High (Phishing-resistant) |
| App with Number Matching | High | Moderate |
| App with One-Time Code | Moderate | Low |
| SMS / Voice Call | Low | Very Low |
| Push Notification | Low | Low (Susceptible to "push fatigue") |
To further strengthen access controls, pair MFA with Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC). For example, remove administrator privileges from standard user laptops to block unauthorized software installations. Implement conditional access policies that require extra verification based on factors like location, device compliance, or network trust levels. Providing employees with a password manager can also promote the use of long, unique, and random passwords for every account.
Once access controls are in place, the next priority is keeping systems up to date.
Ensure Regular Software Updates and Patching
Consistent software updates are essential to prevent attacks. Nearly 60% of cyberattack victims admit that applying a patch could have stopped their breach. With vulnerabilities being the entry point in 20% of data breaches and the average U.S. breach costing $9.36 million, delaying patches is a costly mistake.
To avoid delays, use automation and establish clear maintenance schedules. Prioritize updates based on the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, and test patches in a controlled environment before deployment.
Define emergency maintenance windows for zero-day vulnerabilities and standard monthly updates. Automated tools can help identify missing patches and streamline deployments, reducing manual effort and "patch fatigue." Tailor patching priorities based on system risk levels; for instance, internet-facing devices should be patched faster than isolated intranet servers.
| Technology Type | Recommended Patching Frequency |
|---|---|
| Windows Systems | Monthly (Second Tuesday of each month) |
| Linux Systems | Monthly |
| Network Infrastructure | Quarterly |
| Critical/Zero-Day Flaws | Immediately / Emergency Window |
Outdated software or hardware that no longer receives security updates should be replaced. Unsupported systems are vulnerable by design, and no firewall can compensate for these risks. Enable automatic updates wherever possible, and implement a policy requiring regular device reboots to apply pending updates. For smaller businesses, migrating on-premises mail and file storage to secure cloud platforms like Microsoft 365 can shift the patching responsibility to trusted vendors.
Encrypt Sensitive Data and Secure Backups
Encryption is your defense for protecting data both at rest (stored on devices or servers) and in transit (during transmission). Encrypt entire drives, servers, and critical files, and enable disk encryption on Windows and Mac laptops.
Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule: keep 3 copies of your important files, store them on 2 different types of media (e.g., local drives and the cloud), and ensure 1 copy is stored off-site. This strategy helps protect against hardware failures, natural disasters, and ransomware attacks. Use offline or immutable backups that malware cannot alter or delete. Critical systems, like Active Directory Domain Services domain controllers, should be prioritized for backups to enable swift recovery.
Regularly test your restoration process to ensure recovery can be completed within seven days. Create a detailed recovery plan that outlines backup schedules (continuous, hourly, or weekly) and includes critical contact information in case the network is down. Identify your most essential data – financial records, customer information, and intellectual property – and ensure these are backed up with the highest priority.
With these protection measures in place, you’ll be better prepared to detect and respond to emerging threats effectively.
Detection and Monitoring Checklist
Even with strong defenses in place, no system is completely immune to attacks. That’s why keeping a close watch on potential threats is critical for catching issues early. With nearly half (46%) of all cyber breaches affecting businesses with fewer than 1,000 employees, smaller organizations simply can’t afford to ignore the importance of continuous monitoring. Adding to your existing protection measures, using Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools can provide the visibility needed to identify and respond to new threats.
Deploy Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools
SIEM tools bring together log data from various sources, making it easier to analyze threats in one centralized location. This unified approach helps uncover patterns and connections between events that might otherwise go unnoticed.
"SIEM tools help organizations identify and respond to cybersecurity threats with the urgency they demand, acting as both a robust line of defense and a path to regulatory compliance." – Coursera Staff
Before rolling out a SIEM solution, it’s important to define your goals. Are you looking to improve threat detection? Meet compliance requirements for regulations like GDPR or HIPAA? Or perhaps you want better visibility into your network? Once your objectives are clear, map out your data sources and prioritize logs from key systems first – such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools, operating system logs (Windows and Linux), and logs from cloud or network devices. Keep in mind that SIEM costs often depend on the volume of data processed, so being selective about what you ingest can help control expenses.
For organizations without dedicated security teams, Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) can offer enterprise-level SIEM capabilities without the need to build and maintain the infrastructure yourself. Popular platforms like Microsoft Azure Sentinel, Splunk, and IBM QRadar are widely used for this purpose.
Once your logs are centralized, the next step is to actively monitor for anomalies and set up alerts.
Set Up Alerts and Anomaly Detection
Automated alerts are a key feature of SIEM tools. Configure these to flag high-risk activities, such as unauthorized access to privileged accounts, failed login attempts from unusual locations, privilege escalation, or unexpected changes to critical system configurations. Many modern SIEM solutions use machine learning and behavioral analytics to detect threats that don’t follow traditional patterns, making it easier to identify more sophisticated attacks.
Pay attention to both host-based irregularities (like unusual process hierarchies, attempts to access credentials such as LSASS, or unexpected scheduled tasks) and network-based anomalies (like unauthorized RDP/SSH access, DNS tunneling, or unusual outbound traffic). Defense evasion tactics – such as clearing event logs, disabling firewalls, or stopping security monitoring agents – should also be on your radar.
To avoid being overwhelmed by irrelevant alerts, fine-tune your configurations based on feedback. This reduces the chances of missing critical issues amidst a flood of false positives.
Conduct Regular Log Audits
Regular log audits are a crucial complement to automated alerts. While alerts catch immediate threats, scheduled reviews can help identify long-term patterns or signs of compromise. For high- or moderate-risk data, forwarding logs in real time to your SIEM ensures continuous monitoring. Conduct these reviews regularly to establish a baseline for normal behavior and detect unauthorized access attempts.
For smaller businesses, a quarterly review of security logs – covering firewalls, antivirus software, and other systems – is a sensible starting point. Additionally, log reviews should be performed during system onboarding, after major security incidents, or on a quarterly or annual basis. Sensitive log data access should also be reviewed at least once a year to ensure only authorized personnel have viewing or modification rights.
"Early detection of unusual activity is key to preventing data breaches, ransomware, and other costly incidents." – CISA
To protect the integrity of your logs, restrict access so that no individual is solely responsible for reviewing their own activity. Train your IT and security teams to recognize suspicious patterns in logs and understand their role in the incident response process. Establishing a baseline for normal system activity through regular monitoring makes it easier to spot when something is off. Additionally, test your detection rules regularly with penetration testing to ensure alerts are triggered during simulated attacks.
If you’re looking for expert advice to refine your detection and monitoring strategies, Equifier provides customized cybersecurity consulting and risk assessments to help align these practices with your overall risk management goals.
Response and Recovery Checklist
Having strong detection measures is just the beginning. A solid response and recovery plan can significantly reduce downtime and minimize damage when incidents occur. Statistics show that while 54% of organizations have a disaster recovery plan in place, fewer than 7% can recover from ransomware in a single day. For small businesses, recovery can stretch to three months or longer.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan lays out clear steps for managing security events. The NIST 6-Phase Framework – Preparation, Detection & Analysis, Containment, Eradication, Recovery, and Lessons Learned – provides a structured approach. Assign specific roles to team members, such as:
- Incident Commander: Makes key decisions during the response.
- Technical Lead: Focuses on remediation efforts.
- Communications Coordinator: Handles messaging with stakeholders and media.
- Documentation Specialist: Tracks evidence and logs actions taken.
Your plan should include an up-to-date inventory of critical assets – customer databases, financial records, servers, cloud accounts, and essential business processes. Establish reliable communication protocols, including backup channels like Signal or WhatsApp, in case primary systems like email or Slack are compromised. Clearly define incident priorities to help your team respond appropriately. For example, a single phishing email might only require monitoring, while active ransomware demands immediate action.
| Incident Priority | Criteria | Response Time |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Single phishing email caught by filters; minor glitches. | Monitor |
| Medium | Multiple failed logins; contained malware detection. | 4 hours |
| High | Confirmed malware; suspected data breach; BEC attempts. | Immediate |
| Critical | Active ransomware; confirmed data exfiltration; operations halted. | All-hands |
When an infection is detected, disconnect the affected device from the network without shutting it down – its memory (RAM) may contain critical forensic evidence. Block suspicious IPs at the firewall, disable compromised accounts, and isolate impacted systems. After containing the threat, identify the root cause, remove malicious software, delete unauthorized accounts, and patch vulnerabilities. Restore systems in order of importance, starting with critical functions like accounting and customer management, followed by core operations like email, and finally supporting systems. Keep an emergency "Response Kit" on hand, stocked with tools like forensic imaging software (e.g., FTK Imager), malware scanners, and printed emergency contact lists.
Once your plan is in place, test it to ensure it works effectively under real-world conditions.
Test Disaster Recovery Processes
Having a written recovery plan is not enough – it must be tested regularly to uncover potential gaps. Testing can reveal issues like corrupted backups, incomplete restores, or broken permission settings. Simulate a full recovery by restoring backups to your recovery infrastructure and timing the process. This can also help identify network bottlenecks and verify whether your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) are realistic.
Before restoring data, verify backup integrity on an isolated system to ensure backups aren’t infected. Tools like rsync with the --dry-run option can compare files without making changes. Conduct tabletop exercises with your team to ensure everyone understands their roles and decision-making authority.
Track and Review Security Incidents
Every incident is an opportunity to improve your defenses. Document key details, including how the issue was detected, its root cause, and the steps taken to resolve it. Aim to hold a "Lessons Learned" meeting within 72 hours of resolving an incident to evaluate what worked and what didn’t. Metrics to track include:
- Time from detection to containment
- Time from containment to eradication
- Number of systems impacted
- Total man-hours spent
- Costs of external resources
"A lessons learned meeting involving all relevant parties should be mandatory after a major incident and desirable after less severe incidents with the goal of improving security as a whole and incident handling in particular." – JJ Cranford, Senior Manager of Product Marketing, CrowdStrike
Capture system images and memory from affected devices for forensic analysis. Use these reports as training material for new employees and to refine future drills. Update your recovery playbooks based on internal incidents and insights from other organizations. Before systems go back into production, deploy monitoring tools to ensure they are free of malware or backdoors. Regular reviews keep your response plan up-to-date with evolving threats.
For businesses looking for expert help in building effective response and recovery strategies, Equifier offers tailored cybersecurity consulting and risk assessments to fit your specific needs and compliance goals.
Employee Training and Compliance Checklist
Technical defenses are essential, but they can’t stand alone. Human awareness and strict adherence to procedures are equally critical for a strong cybersecurity strategy. With 75% of data breaches involving human error, your employees can be your best defense – or your greatest vulnerability. A well-educated staff paired with strong compliance measures can significantly cut breach costs, saving as much as $232,867. Organizations with trained incident response teams that regularly test their plans save an average of $2.66 million.
Implement Regular Training Programs
Cybersecurity training isn’t a one-and-done task – it needs to be ongoing. Employees should be educated on advanced phishing tactics, social engineering (like deepfakes), and basic cyber-hygiene practices such as safe browsing, password management, and secure data handling. Quick identification and reporting of potential threats can stop incidents from escalating.
"All breaches begin with the human factor; putting in the effort to harden those vectors for attack is equally if not more important than any software or hardware hardening." – Mathew Everman, Information Security Operations Manager at CIS
To ensure the lessons stick, use a mix of learning formats – reading materials, videos, interactive exercises, and phishing simulations. High-risk departments, such as finance, IT, and executive teams, should get tailored training to address the specific threats they face. A 2023 study revealed that 75% of remote workers in companies without training programs still have access to sensitive data, underscoring how vital comprehensive training is. Keep detailed records of training sessions, including dates, attendance, and topics, to support audits.
Once training is in place, reinforce it by aligning your operations with established industry standards.
Ensure Compliance with Industry Standards
Frameworks like SOC 2 and ISO 27001 offer clear guidelines for building a solid security program. SOC 2, created by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA), focuses on five Trust Services Criteria: Security (mandatory), Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy. A SOC 2 Type II audit evaluates whether your controls are effectively implemented over a period of 3 to 12 months, demonstrating operational maturity.
Start with a gap analysis to identify weaknesses, prioritize fixes, and schedule regular reviews – monthly or quarterly – to ensure continuous compliance. Maintain a centralized repository for policies, time-stamped logs, and vendor security reports to simplify audit preparation. Don’t forget about third-party risks. Request SOC reports or security questionnaires from your vendors, as their security posture directly impacts your compliance efforts.
For businesses needing extra support, Equifier offers consulting services for compliance audits and implementation, helping organizations navigate frameworks like SOC 2 and ISO 27001 with ease.
Establish Access Management Processes
Managing access is about controlling who has permission to do what – and when. Use Joiner-Mover-Leaver (JML) protocols to manage access rights throughout an employee’s lifecycle. For new hires, conduct background checks and grant access based on their specific job role using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). When employees switch roles, update their permissions immediately to match their new responsibilities. And when someone leaves, revoke all access on their last day – no exceptions.
Apply the Principle of Least Privilege, ensuring employees can only access what they truly need. Centralized Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems can streamline user authentication and privilege assignments across the organization. Regular audits of user permissions can help identify and address orphaned accounts or excessive privileges before they become security risks.
Audit and Continuous Improvement Checklist
Once you’ve established risk mitigation measures, the next step is ensuring your cybersecurity strategy stays effective. Cybersecurity threats, technologies, and business needs are constantly changing, so your defenses need to keep up. Regular audits, combined with a focus on continuous improvement, help you maintain a strong and relevant security posture. Organizations that perform quarterly cybersecurity audits can spot vulnerabilities before attackers do, and by acting on these findings, they systematically lower their risk over time.
Conduct Quarterly Cybersecurity Audits
Every three months, take a close look at your security controls to uncover and address vulnerabilities early. Start with a policy and compliance review to ensure your cybersecurity policies are up-to-date, well-documented, and effectively communicated throughout your organization. Verify compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. Perform an access control audit to check user permissions, manage privileged accounts, and confirm that multi-factor authentication (MFA) is enabled for critical systems.
Ensure sensitive data is encrypted both when stored and while being transmitted. Review your firewall and Intrusion Detection System (IDS) settings, confirm antivirus software is current on all devices, and make sure your patch management process is running smoothly.
"Cybersecurity is an evolving field, and regular audits are critical to maintaining a strong security posture." – Cybersecure California
Track performance metrics to measure your security effectiveness. Targets might include 95% or more devices with up-to-date security patches, 100% employee adoption of password managers, detecting incidents within 24 hours, and containing threats within 72 hours. To complement your internal audits, conduct annual penetration tests – automated scans may miss vulnerabilities that skilled testers can uncover.
These audits provide the foundation for continuous improvement, ensuring that every identified risk is addressed without delay.
Analyze and Prioritize Audit Findings
Once your audit is complete, it’s time to dive into the results. Analyze the findings immediately to identify the root causes of vulnerabilities. Categorize the issues by severity – Critical, High, Medium, or Low – so you can focus on the most urgent risks first. A risk matrix can help you prioritize by plotting the likelihood of an issue against its potential impact, ensuring you address high-probability, high-impact risks first.
Develop a clear action plan for each issue. This plan should outline specific steps, assign responsibilities, identify necessary resources, and set firm deadlines. Cyber risks aren’t isolated IT problems – they should be integrated into your organization’s broader risk management strategy to balance them with other operational priorities.
"If you don’t act on your audit findings, your organization risks losing applicable certifications and, by extension, suffering reputational damage." – Sean Atkinson, Chief Information Security Officer, CIS
Leverage automated tools to monitor the effectiveness of your changes and visualize progress over time. Assign tasks to specific team members using assessment tools to ensure accountability and follow-through.
Update Cybersecurity Policies and Procedures
Your cybersecurity policies must evolve to counter new threats like AI-driven attacks, advanced phishing schemes, and vulnerabilities in operational technology. Review and update your security checklists and procedures quarterly to keep pace with emerging risks, technological advancements, and changing business needs. Regular updates also help you stay compliant with shifting legal requirements, avoiding penalties and maintaining trust.
Align your security protocols with departmental workflows to minimize disruptions and encourage adoption. Since 43% of business data loss is linked to insider threats and human error, updated procedures can empower employees to act as a first line of defense. As your organization implements new tools like remote access systems, BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies, or third-party cloud integrations, adapt your policies to address the risks these technologies bring.
Use a month-by-month roadmap to gradually strengthen your cybersecurity practices, avoiding the chaos of large-scale overhauls. Automate compliance tracking with security awareness platforms to manage employee risk and meet regulatory requirements without adding manual work. Clearly outline the consequences of policy violations so employees understand the importance of compliance. Findings from one quarter should inform training and policy updates for the next, helping you stay ahead of evolving threats.
Conclusion
This checklist serves as your guide to building a strong and effective cybersecurity framework. By focusing on identifying assets, managing vulnerabilities, and prioritizing risks, you can prevent up to 99% of common exploits and significantly reduce breach-related costs. For organizations relying on checklist-based risk assessments, this approach can help avoid average breach expenses that now exceed $4.45 million globally, aligning your security efforts with your business goals.
Think of your checklist as a living document. Regular updates, ongoing employee training, and a commitment to continuous improvement ensure your defenses stay ahead of ever-evolving threats. Proactive measures like firewalls, multi-factor authentication, encryption, and access controls are essential for stopping threats early, helping to mitigate risks in a cost-efficient way. These actions reinforce the key pillars of risk management: identification, protection, monitoring, response, training, and ongoing refinement.
Expert guidance can make all the difference. Specialized support can provide thorough risk assessments, compliance advice, and tailored strategies to help you choose the most effective controls and develop strong incident response plans. This level of expertise elevates your efforts from merely ticking boxes to building a truly resilient cybersecurity strategy.
Equifier’s cybersecurity consulting offers the expertise you need to bring this checklist to life. From conducting vulnerability assessments to enhancing IT infrastructure and cloud solutions, their tailored services ensure your organization is prepared to tackle today’s cybersecurity challenges.
FAQs
How often should a business conduct cybersecurity risk assessments?
Businesses should conduct cybersecurity risk assessments at least annually to stay prepared for potential threats and align with industry standards. However, if your organization has a higher risk profile, faces specific regulatory requirements, or has recently undergone changes in its IT environment, it might be wise to schedule these assessments more frequently – think quarterly or semi-annually.
Keeping cybersecurity assessments up to date allows you to uncover vulnerabilities, tackle new threats, and maintain a solid defense. Being proactive not only safeguards sensitive information but also helps reduce the chances of expensive breaches or operational disruptions.
What are the best ways to train employees on cybersecurity risks?
The best approaches to employee cybersecurity training emphasize developing both awareness and hands-on skills to spot and stop cyber threats. Key areas to focus on include recognizing phishing attempts, setting up strong passwords, and managing sensitive data securely.
Frequent training sessions, paired with simulated exercises, allow employees to practice handling realistic scenarios. Continuous education is also essential to keep them informed about emerging threats and updated security practices. By creating a workplace culture that prioritizes cybersecurity awareness, companies can greatly minimize the chances of breaches caused by human error.
What are some cost-effective ways small businesses can improve their cybersecurity?
Small businesses can boost their cybersecurity without overspending by focusing on a few smart, practical steps. Start by maintaining an up-to-date list of all your hardware, software, and data assets. This helps you spot potential weak points and manage risks more effectively.
Implementing strong password practices is another easy win. Change default passwords, make them hard to guess, and enable multi-factor authentication to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Keeping your software current is equally important. Regular updates and applying security patches can protect your systems from known vulnerabilities. On top of that, offering basic security awareness training to your team can go a long way in minimizing human errors – one of the leading causes of security breaches.
Lastly, make it a habit to back up your critical data regularly and establish clear cybersecurity policies. These measures are affordable but can play a big role in safeguarding your business from potential threats.