End-to-end (E2E) tests are critical for ensuring that your software works as a complete system. While unit tests are fast and effective for checking individual code components, they miss critical integration issues that can arise when different parts of your application interact. E2E tests simulate real user workflows, such as logging in, completing a purchase, or processing payments, to uncover problems that unit tests cannot detect.
Key Takeaways:
- Unit Tests: Focus on isolated functions or components; fast but limited to catching small-scale issues.
- End-to-End Tests: Validate entire workflows, ensuring components, APIs, databases, and third-party services work together seamlessly.
- Why E2E Tests Matter: They catch bugs in user flows, reduce production errors, and ensure a better user experience.
By combining unit tests for small-scale validations with E2E tests for broader workflows, you create a reliable testing framework that balances speed and thoroughness. Start by testing your application’s most critical user journeys, such as login and checkout processes, to prevent costly failures in production.
The Problem: Unit Tests Miss Critical Issues
Unit Tests Don’t Simulate Actual Usage
Unit tests are great for checking if individual functions or classes work as expected, but they don’t reflect how users actually interact with your software. For instance, testing a login function might confirm that password validation works, but it doesn’t guarantee the entire authentication process functions correctly. While unit tests focus on isolated pieces of code, users care about whether the system delivers the results they need.
Here’s the kicker: mocks can make it seem like everything is fine. You might achieve 100% unit test coverage using mocks, but that doesn’t mean your system will work in the real world. A perfectly tested function might still fail when integrated into a larger workflow. This gap leaves critical integration issues hidden beneath the surface.
Integration Problems Go Undetected
Unit tests are not equipped to catch problems in the connections between components – things like API calls, database interactions, or third-party integrations. Even if every individual unit works flawlessly, failures in how these units interact can bring the entire system crashing down.
"Unit tests are incapable of ensuring that when you call into a dependency that you’re calling it appropriately (though you can make assertions on how it’s being called, you can’t ensure that it’s being called properly with a unit test)." – Kent C. Dodds, Software Engineer
Some of the trickiest bugs only show up when the system runs as a whole. Misaligned contracts between components, timing issues in asynchronous tasks, or data consistency problems across subsystems often remain undetected when relying solely on unit tests.
User Experience Suffers in Production
The limitations of unit tests don’t just affect developers – they directly impact users. When workflows aren’t thoroughly tested, bugs and crashes inevitably show up in production. Imagine a checkout process that fails, welcome emails that never get sent, or dashboards that display incorrect data. These issues stem from untested workflows that unit tests simply can’t cover.
"If you have too few [end-to-end tests], subtle bugs will creep through to production, despite a fast test suite with 100% code coverage." – David Copeland, Director of Engineering, Stitch Fix
The result? Frustrated users, lost revenue, and damaged trust. While unit tests can create an illusion of security, they often leave critical workflows unchecked, allowing avoidable issues to impact production.
sbb-itb-05efa2a
End to End Testing – Explained
Unit Testing vs End-to-End Testing: Key Differences
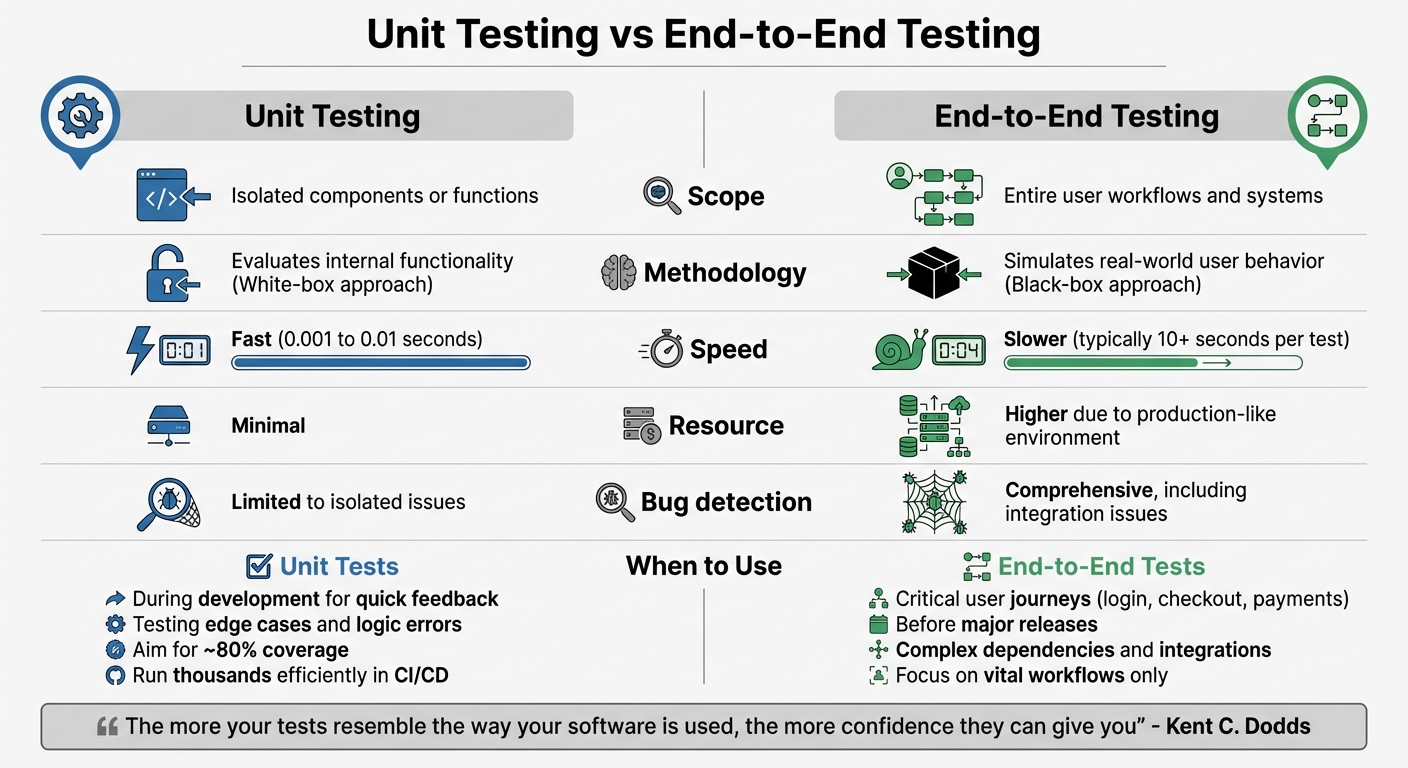
Unit Testing vs End-to-End Testing: Key Differences and When to Use Each
Understanding the differences between unit tests and end-to-end tests helps refine your testing strategy. Unit tests focus on small, isolated pieces of code – like individual functions, methods, or classes – ensuring each component works as intended on its own. In contrast, end-to-end (E2E) tests validate complete workflows, simulating how users interact with your application across various subsystems, APIs, databases, and integrations.
The approaches differ significantly. Unit testing uses a white-box method, diving into the internal logic of your code. Meanwhile, end-to-end testing takes a black-box approach, focusing on user behavior without delving into the underlying code. As Kent C. Dodds aptly puts it, "The more your tests resemble the way your software is used, the more confidence they can give you". This distinction highlights why a balanced testing strategy is crucial for building reliable software.
Comparison Table: Unit Testing vs End-to-End Testing
| Aspect | Unit Testing | End-to-End Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Isolated components or functions | Entire user workflows and systems |
| Methodology | Evaluates internal functionality | Simulates real-world user behavior |
| Execution Speed | Fast (0.001 to 0.01 seconds) | Slower (typically 10+ seconds per test) |
| Resource Needs | Minimal | Higher due to production-like environment |
| Bug Detection | Limited to isolated issues | Comprehensive, including integration issues |
These differences make each method suitable for specific purposes, depending on your goals.
When to Use Each Testing Approach
Combining unit and end-to-end testing ensures a robust testing framework. Unit tests are your go-to during development. They catch logic errors early, test edge cases (like a coupon code calculator), and provide near-instant feedback. Since they’re fast, you can run thousands of them efficiently in your CI/CD pipeline. Aiming for around 80% unit test coverage is a common benchmark.
End-to-end tests, on the other hand, are essential for verifying critical user journeys – like login flows, checkout processes, or payment gateways – before major releases. These tests are especially important for applications with complex dependencies, such as external APIs, databases, or third-party integrations, where unit tests often rely on mocks. However, because E2E tests are slower and require production-like environments, they should focus on the most vital workflows rather than attempting to cover every detail.
As Tim Bray, former Distinguished Engineer at AWS, remarked, "Testing – and testing culture more broadly – is the ‘biggest single contributor to improved software in [my] lifetime’". By balancing unit and end-to-end testing, you can ensure both speed and reliability in your development process.
The Solution: End-to-End Testing
What End-to-End Testing Does
End-to-end (E2E) testing checks every part of your application – from the user interface all the way to the back end, including databases and third-party APIs. Instead of focusing on isolated components, E2E tests simulate a complete user experience, like signing up for an account, using a shopping cart, or completing a checkout process. This ensures that all parts of the system work together as expected.
These tests run in staging environments that mimic production, catching integration issues that unit tests often miss. While unit tests rely on mocked data, E2E tests interact with actual databases, API calls, and external services like payment gateways or email systems. By replicating real-world conditions, E2E testing helps detect problems that only appear during full-system interactions.
How End-to-End Tests Fill the Gaps
E2E testing goes beyond basic validation by addressing critical blind spots in isolated testing. It identifies "emergent" bugs – those that only appear when different components work together. For instance, a payment function might pass unit tests but fail to update the database or send a confirmation email when combined with other systems.
The cost savings are undeniable. Fixing a bug in production can be up to 100 times more expensive than resolving it during development. E2E tests serve as a safety net before release, protecting both your users and your budget. Adrian Sutton, former Lead Developer at LMAX, highlighted this benefit:
"End-to-end tests allowed the team to try daring things and make sweeping changes, confident that if anything is broken it will be caught".
This level of confidence empowers development teams to innovate and make significant changes without compromising reliability.
Why End-to-End Testing Matters
End-to-end (E2E) testing steps in where unit tests fall short, ensuring your application operates reliably as a whole.
Complete Coverage of Application Workflows
While unit tests focus on individual components, E2E tests validate how everything works together. They check entire user workflows – from clicking a button to saving data in the database and sending confirmation emails – capturing integration issues that unit tests often miss.
For instance, unit tests might confirm that your login function works in isolation, but E2E testing ensures it grants access to the user dashboard, loads saved preferences, and interacts correctly with your authentication service. These broader system behaviors are hard to test with unit tests alone, as they usually rely on mocked dependencies.
By addressing these gaps, E2E testing ensures your application delivers a seamless experience.
Better User Experience Through Realistic Testing
E2E testing mimics real user actions – like navigating pages, filling out forms, and completing transactions – to uncover UI glitches, workflow problems, and integration errors that can disrupt the user experience. It tests the interface alongside the business logic, ensuring everything displays and functions as expected. Plus, E2E tests verify your app’s stability across various platforms, checking performance on different browsers, devices, and operating systems.
Fewer Errors and Less Downtime
E2E testing doesn’t just improve usability – it also reduces costly production errors. By validating critical workflows like payment processing and user registration under real-world conditions, E2E testing helps prevent disruptions that could hurt your bottom line. It also catches environment-specific problems, such as expired credentials, security access issues, or connectivity failures with external services – problems that might otherwise lead to emergency fixes and lost revenue.
Examples: End-to-End Testing in Practice
E2E tests go beyond addressing the gaps left by unit tests, playing a vital role in ensuring entire systems function as intended. Let’s dive into three practical examples that highlight their importance.
Testing Login Systems
E2E testing ensures the entire identity lifecycle – from sign-up to multi-factor authentication – works smoothly. It validates everything: UI interactions, API calls, session handling, and role-based access permissions. Unlike isolated tests, E2E tests cover critical aspects like session management and access restrictions. For example, they confirm that regular users receive a 403 Forbidden error when attempting to access admin-only areas and verify that session tokens are destroyed upon logout to prevent unauthorized access.
These tests even handle multi-factor authentication by programmatically retrieving one-time passcodes from test email inboxes or virtual authenticator apps. This level of testing is essential because over 50% of users abandon an app after encountering just one bug in a day. Furthermore, failing to meet security standards can cost companies up to $14 million. By covering these intricate workflows, E2E tests protect both the user experience and system security.
Testing Payment Gateways
In 2024, payment failures led to a staggering $1.86 trillion loss in global e-commerce revenue. This highlights the importance of E2E testing for payment systems. These tests catch issues that unit tests miss, such as delayed discount applications, inventory mishandling, or disruptions in external systems. E2E tests can simulate real-world scenarios like network interruptions or flagging by bank algorithms for rapid transactions – problems that are invisible to unit tests.
Testing on actual devices, rather than emulators, uncovers 60% more issues. By validating payment workflows under realistic conditions, E2E testing helps organizations avoid costly production failures and revenue loss.
Testing API Integrations
In distributed systems, a single user action often involves multiple interconnected services. E2E testing ensures these components work together seamlessly. For instance, it validates workflows that link user registration, authentication, data retrieval, updates, and deletion into a single, continuous process.
"Integration testing is about verifying the contract between services. E2E testing is about verifying the promise you made to your user." – TestDriver
E2E tests also ensure data accuracy as it moves through databases, caches, and third-party services, identifying issues in the "glue" that binds system components. Organizations that carefully plan test scenarios can reduce testing time by as much as 60%, making E2E testing both thorough and efficient. This approach guarantees that distributed systems deliver a reliable experience to users.
Conclusion: Why You Need End-to-End Testing
Key Takeaways
Unit tests focus on verifying individual functions or components, but they often miss issues that arise when these pieces work together. That’s where end-to-end (E2E) testing steps in, ensuring that entire workflows function smoothly from the user’s perspective. This approach uncovers integration bugs, data inconsistencies, and configuration problems that unit tests might overlook.
By mimicking real user interactions – like logging in, completing a purchase, or interacting with APIs – E2E testing ensures your application delivers a seamless and dependable experience. It’s an essential part of maintaining software quality and supporting development teams as they innovate.
With a solid E2E testing suite in place, developers can confidently refactor code and roll out updates faster, knowing that critical workflows are safeguarded. This confidence is key to balancing innovation with stability.
Getting Started with End-to-End Testing
Begin by focusing on the workflows that matter most. Identify your application’s critical user journeys – such as login processes, checkout flows, or payment systems – where failures could have a major impact on your users or business. Use stable selectors like data-* attributes to make tests more reliable, and design them to run independently. This allows for parallel execution, speeding up the feedback process.
To maximize the value of E2E testing, integrate it early into your CI/CD pipeline. Pair about 80% unit test coverage with targeted E2E tests for key workflows. This combination strikes a balance between speed and reliability. Automating repetitive tasks reduces human error and ensures consistent test execution. The goal isn’t to achieve perfection but to deliver software that performs as users expect.
FAQs
How many end-to-end tests do I need?
The number of end-to-end tests required hinges on how complex your application is and the workflows it supports. Prioritize testing critical user scenarios and key integrations to ensure everything runs smoothly and reliably for users. The goal is to create a thoughtful set of tests that confirm essential features work as intended – without going overboard or repeating efforts unnecessarily.
Should end-to-end tests hit real third-party services?
End-to-end tests often interact with real third-party services, offering a way to validate workflows and spot integration problems. This approach ensures the tests mirror actual production conditions, giving a more accurate picture of how systems interact in real-world scenarios.
That said, the decision to use real services hinges on your testing goals and setup. Some teams favor this method for its authenticity, while others lean toward mock services to sidestep risks like downtime or unexpected dependencies during testing. Both approaches have their place, depending on the priorities and constraints of your environment.
How do I keep end-to-end tests fast and stable?
To keep end-to-end tests both quick and reliable, it’s important to fine-tune your test design, avoid unnecessary scope expansion, and tackle issues like slow systems or browser-related delays. Stick to best practices such as isolating tests and implementing patterns that resist flakiness. These strategies can help reduce instability while boosting performance.