Your proprietary code base is the backbone of your software. If it’s scattered across multiple repositories and local machines, it creates inefficiencies and security risks. Centralizing your code in GitHub addresses these challenges by providing a single source of truth and enabling powerful tools like GitHub Actions for automation.
Key Takeaways:
- Centralized Code Management: GitHub simplifies collaboration, enforces consistent standards, and improves security with features like branch protection and secret scanning.
- Automated Security: Tools like Dependabot, CodeQL, and secret scanning help identify vulnerabilities and manage dependencies.
- Streamlined Deployments: GitHub Actions automates testing, builds, and deployments, reducing errors and saving time.
- Access Control: Permissions, CODEOWNERS files, and environment-level secrets ensure sensitive data stays protected.
To secure and streamline your development process, GitHub provides the tools you need to manage your code base, automate workflows, and enhance security – all in one place.
Complete GitHub Actions Course – From BEGINNER to PRO
How to Structure Your Code Base in GitHub
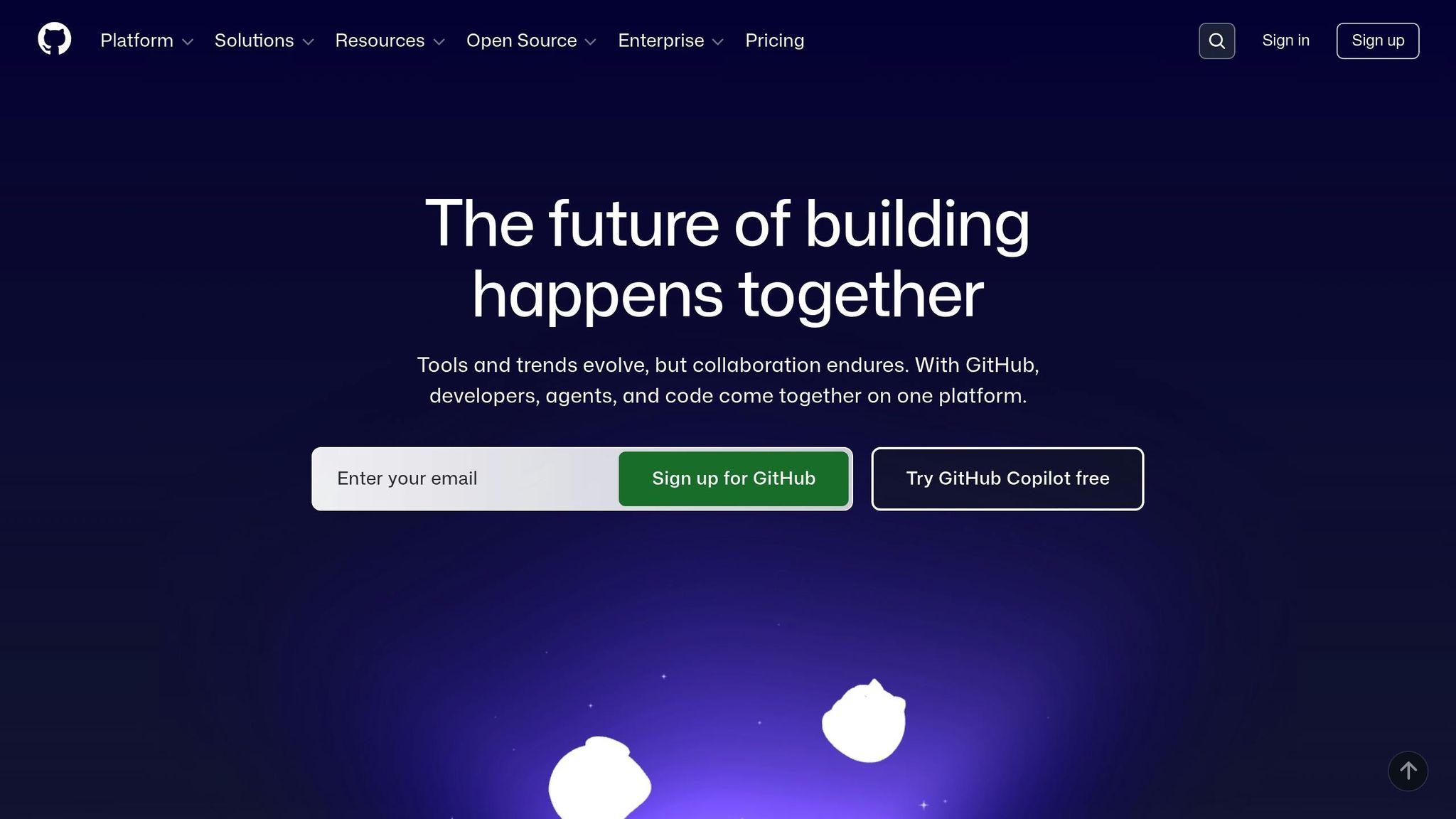
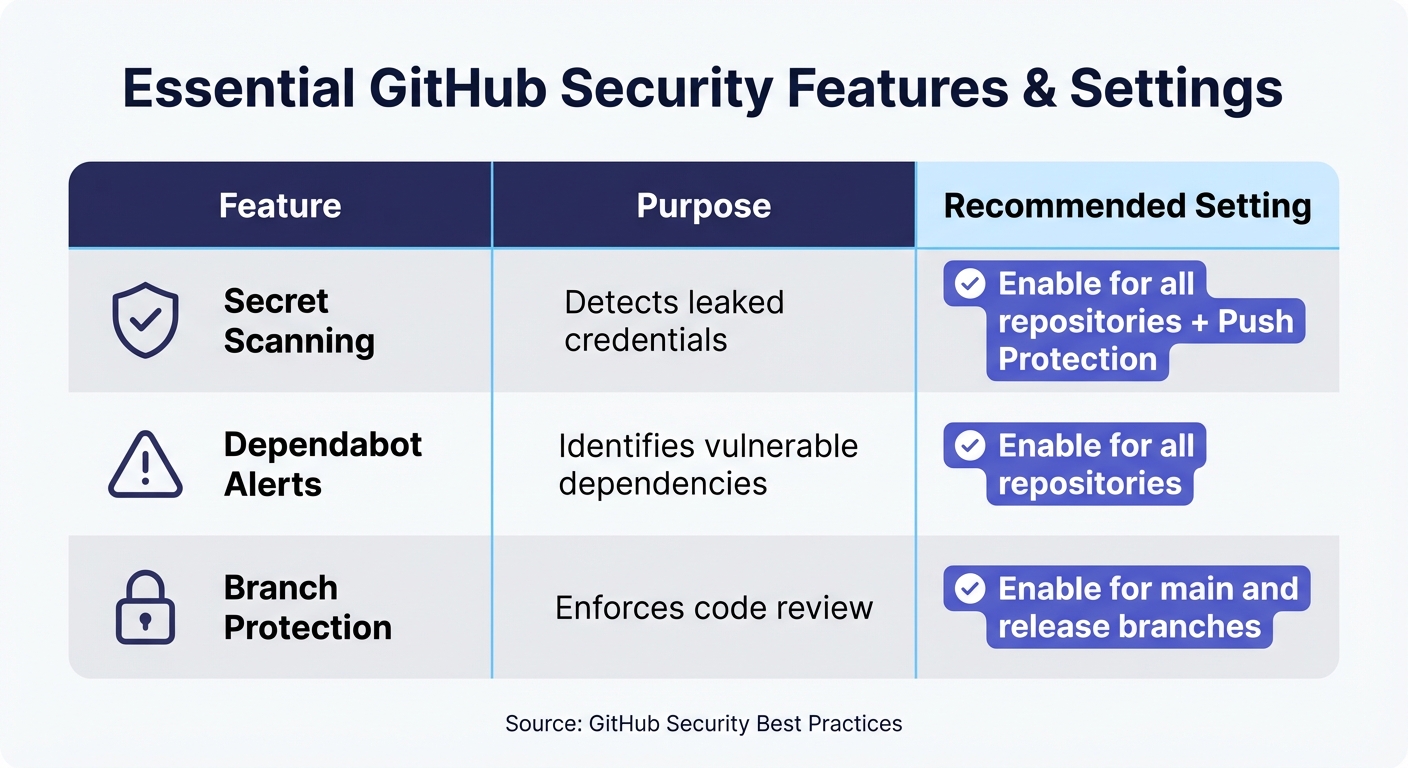
GitHub Security Features Comparison: Key Tools and Recommended Settings
Setting Up a GitHub Organization
Creating a GitHub Organization isn’t just about organization – it’s a practical way to manage security at scale. With the "Security coverage" view, you can monitor and apply security settings across all repositories at once. This eliminates the hassle of configuring each repository individually, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
Security features like secret scanning and Dependabot can be set to activate automatically for new repositories. This means that when developers create a new repo, these protections are already in place – no manual setup required. It’s a simple way to avoid leaving new code exposed.
To manage security without giving away full owner permissions, assign the "security manager" role to your IT or security team. This role lets them handle security settings and monitor alerts across all repositories while following the principle of least privilege.
For better organization, group repositories by product or team using nested teams. For example, you might have an "Engineering" team with sub-teams like "Backend", "Frontend", and "DevOps." This structure grows with your organization while keeping permissions manageable.
Once your organization is set up, the next step is defining repository standards to ensure consistency and security.
Repository Standards You Should Follow
Every repository should include three key files: README.md, SECURITY.md, and LICENSE.md. The README explains the project to developers, the SECURITY.md outlines how to report vulnerabilities, and the LICENSE.md clarifies how the code can be used.
Protect your main branch by setting branch protection rules. These rules enforce pull request reviews and require successful status checks before merging. This way, untested code never makes it to production. For proprietary projects, stick to a branching workflow instead of forking. Keeping everything within a single repository ensures visibility and control.
Enable "Push protection" to catch accidental commits containing secrets before they land in your repository. For projects with large files like binaries or datasets, use Git Large File Storage (LFS) to maintain repository performance.
Here’s a quick overview of important features and their recommended settings:
| Feature | Purpose | Recommended Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Secret Scanning | Detects leaked credentials | Enable for all repositories + Push Protection |
| Dependabot Alerts | Identifies vulnerable dependencies | Enable for all repositories |
| Branch Protection | Enforces code review | Enable for main and release branches |
With these standards in place, you can focus on fine-tuning permissions and visibility.
Managing Permissions and Visibility
To keep sensitive data secure, apply detailed access controls. Use the "Manage access" settings to grant permissions to specific teams or individuals instead of applying broad access across your organization. Adjust repository visibility (public, private, or internal) in the "Danger Zone" settings based on your requirements.
Set the default permissions for the GITHUB_TOKEN to read-only for repository contents. If a workflow needs additional permissions, grant them only for that specific job. This reduces the risk if a workflow is ever compromised.
For sensitive file changes, use a CODEOWNERS file to enforce expert reviews. For example, if someone modifies a workflow in .github/workflows or updates a critical configuration, the security team must approve it before merging.
If your organization uses self-hosted runners, group them to control which repositories can access specific runner environments. This limits the potential damage from a compromise.
Finally, require environment-level secrets and designated reviewers for deployment workflows. Sensitive credentials should stay locked until an authorized person approves the deployment. Regularly audit your secrets and user access lists to remove anything unnecessary. Unused credentials are risks waiting to happen.
Automating Deployments with GitHub Actions
Manual deployments can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Automating workflows with GitHub Actions simplifies the process by triggering specific tasks based on repository events. This automation covers everything from building and testing code to deploying it live, ensuring a smoother workflow and reducing human error.
Workflows can run on GitHub-hosted virtual machines or self-hosted runners, depending on your resource requirements. This flexibility allows you to deploy to cloud providers, on-premises servers, or hybrid setups without altering your automation strategy. With this in place, continuous integration and delivery become much more efficient.
Creating GitHub Actions Workflows
Workflows are defined in YAML files stored in the .github/workflows directory. Keeping these files alongside your code ensures deployment logic is version-controlled and easy to audit. If you’re just starting, GitHub provides templates for common services to help you get going quickly.
You can configure workflows to trigger on specific events like code pushes, pull request updates, or even manual triggers (workflow_dispatch). Use environments such as production and staging to organize deployment targets effectively.
To avoid issues like race conditions during deployments, use concurrency groups. These ensure that only one deployment runs at a time for a specific environment, preventing conflicts when multiple developers push changes simultaneously. Adding cancel-in-progress: true cancels any ongoing deployment if a new one is triggered.
For secure workflows, OpenID Connect (OIDC) can authenticate directly with cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, eliminating the need for storing long-lived credentials as GitHub secrets. This reduces the risk of credential exposure. By default, set the GITHUB_TOKEN permissions to read-only and grant additional permissions only to jobs that require them.
Critical deployments can be gated with deployment protection rules, requiring manual approval from specific reviewers or checks from integrated tools to verify system health before proceeding. If a deployment waits for approval for over 30 days, it automatically fails.
| Feature | Function for IT Teams |
|---|---|
| Environments | Restrict secrets and define protection rules for specific targets like production. |
| Concurrency | Prevents simultaneous deployments to the same resource. |
| OIDC | Authenticates with cloud providers without long-lived secrets. |
| Protection Rules | Requires approvals or external checks before deploying. |
Integrating CI/CD Pipelines
GitHub Actions makes it easy to integrate continuous integration (CI) with continuous delivery (CD). Push-triggered workflows handle building, testing, and deploying code, ensuring every release is verified before going live. Reusable actions from the GitHub Marketplace can simplify repetitive tasks like setting up environments or authenticating with cloud providers, reducing the need for custom scripts.
To secure your workflows, pin third-party actions to a full-length commit SHA rather than a tag. This prevents supply chain attacks caused by malicious tag changes. Tools like Dependabot can help by keeping your actions and workflows up to date with the latest security patches.
Define concurrency at the job level instead of the workflow level. This allows non-deployment tasks, such as linting or running unit tests, to continue even if a deployment is queued. It speeds up feedback for developers. A matrix strategy can further optimize workflows by running the same job across different operating systems or language versions simultaneously, cutting down validation times significantly.
Add workflow status badges to your README file so team members can easily check the success or failure of deployments. You can also integrate with communication tools like Slack or Teams for real-time updates. Workflow run logs provide detailed insights to debug failures and monitor execution times.
For added security and traceability, use artifact attestations. These verify the integrity of your software builds and ensure every deployment is traceable – an essential feature for audit and compliance purposes.
sbb-itb-05efa2a
Improving Security with Automated GitHub Actions
Security vulnerabilities in your code can lead to serious consequences – data breaches, compliance issues, and financial losses. GitHub Actions helps mitigate these risks by automating security checks throughout your development process. Tools like secret scanning and CodeQL analysis detect vulnerabilities early, reducing potential exposure. For example, secret scanning identifies leaked credentials in your commit history. While these features are free for public repositories, private repositories require a GitHub Advanced Security subscription.
CodeQL analysis automatically scans your source code for vulnerabilities and coding errors. You can use the default setup, which detects supported languages automatically, or opt for a more customized configuration with workflow files tailored to your project. Beyond code, the dependency graph tracks packages your project relies on, while Dependabot monitors for vulnerabilities, opening pull requests with fixes when issues are found.
Another layer of protection comes from dependency review, which flags new vulnerabilities introduced by updates during pull requests. This allows your team to address issues during code review instead of after deployment. For additional safeguards, integrating OpenSSF Scorecards into your workflows can highlight risky practices, such as unpinned actions or overly permissive token settings.
These automated checks complement your existing security measures, helping to secure your codebase more effectively.
Automating Code and Dependency Scanning
GitHub Actions also simplifies security scanning, building on automated deployments. To get started, enable CodeQL in your repository settings. The default configuration works for most projects, but if you have specific needs, you can create custom workflow files in the .github/workflows directory. CodeQL supports multiple languages and runs automatically on every push or pull request, providing immediate feedback.
To guard against script injection attacks, avoid using untrusted input (like pull request titles) directly in workflows. Instead, assign such input to temporary variables. This reduces the risk of attackers executing malicious code through crafted pull requests or issue descriptions. Another helpful practice is using the ::add-mask:: command to redact sensitive values from logs, ensuring they don’t appear during workflow execution.
Dependabot ensures your actions and workflows stay up-to-date by automating updates. The dependency review action can block pull requests that introduce vulnerable packages, stopping potential security risks before they enter your codebase.
For authentication, use OIDC to minimize credential exposure. If storing secrets is unavoidable, place production credentials in environment secrets and enforce manual approval gates before granting workflows access.
| Security Feature | What It Does | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| CodeQL Analysis | Scans code for vulnerabilities and errors | Identifying security flaws in code |
| Secret Scanning | Detects leaked credentials in commit history | Preventing credential exposure |
| Push Protection | Blocks commits containing secrets | Stopping leaks at the source |
| Dependency Review | Flags vulnerable packages in pull requests | Catching risks during code review |
Using CODEOWNERS to Control Workflow Security
To further centralize security, CODEOWNERS ensures critical workflow changes are reviewed by the right experts. The CODEOWNERS file assigns specific team members to review changes to designated parts of your repository. Place this file in the repository root or the .github directory, and define ownership rules for the .github/workflows directory. This setup ensures that changes to CI/CD pipelines are reviewed by security or DevOps personnel before they are merged.
By requiring expert approval for workflow changes, you can prevent unauthorized modifications that might introduce vulnerabilities. Setting up branch protection rules to enforce CODEOWNERS review requirements adds an extra layer of oversight, ensuring deployment processes remain secure.
Regularly audit workflow logs to ensure secrets stay redacted. If an unredacted secret is found, remove the log immediately and rotate the secret to minimize exposure. GitHub’s audit log also tracks events like org.update_actions_secret, giving you visibility into who made changes to critical security configurations and when they occurred.
Managing Dependencies with GitHub Actions
Keeping dependencies up to date is critical to reducing security risks and avoiding technical debt. GitHub’s Dependabot plays a key role here by identifying outdated or vulnerable packages and automatically generating pull requests to address them. Even if GitHub Actions is disabled at the repository or organization level, Dependabot still runs on Actions runners, ensuring essential security patches are never delayed. This makes it a perfect addition to your deployment and security workflows.
To enable Dependabot, you’ll need to add a dependabot.yml configuration file to the root of your repository. This file allows you to manage both version updates and security patches in one place. For repositories using private registries, authentication tokens can be securely stored as encrypted secrets.
GitHub Actions can also streamline how you handle Dependabot pull requests. For example, the dependabot/fetch-metadata action extracts important details – such as the dependency name and whether the update is a major, minor, or patch change. This data can be used to automatically label pull requests, run specific test suites, or even approve and merge updates that meet predefined criteria. Additionally, the Dependency Review Action provides visual insights in the "Files Changed" tab, helping you assess the impact of updates. For workflows using third-party actions, enabling Dependabot ensures those tools are kept current as well.
Automating Dependency Updates and Vulnerability Checks
Dependabot’s automated pull request system works hand in hand with the dependency graph to enhance security. The dependency graph tracks all the packages your project uses, categorizing them by vulnerability severity and linking directly to relevant advisories [6, 26]. When Dependabot identifies a vulnerable dependency, it creates a pull request to update it to the minimum version that resolves the issue [6, 26].
Here are some key features that benefit proprietary codebases:
| Feature | Function | Benefit for Proprietary Code |
|---|---|---|
| Dependabot Version Updates | Updates manifest files to the latest versions | Reduces technical debt and keeps internal tools up to date |
| Dependabot Security Updates | Fixes dependencies with known vulnerabilities | Lowers the attack surface of proprietary software |
| Dependency Review Action | Scans pull requests for new vulnerabilities | Prevents security flaws from reaching the main branch |
You can use GitHub Actions to automate the triage process for Dependabot pull requests. For instance, workflows can automatically merge low-risk patch updates while flagging major changes for manual review. Alerts are powered by the GitHub Advisory Database, which offers a searchable collection of security advisories that trigger these automated updates [6, 26].
Securing Third-Party Actions
Managing dependencies is only part of the equation. Ensuring the integrity of the tools that handle these updates is just as important. Third-party actions, while useful, can introduce supply chain risks. To minimize these risks, always pin actions to their full-length commit SHAs instead of using version tags. For example, use actions/checkout@a81bbbf8298c0fa03ea29cdc473d45769f953675 rather than actions/checkout@v3. Commit SHAs are immutable, unlike tags, which can change over time [6, 26].
For added security, use OIDC for cloud authentication and set the GITHUB_TOKEN to read-only by default. Grant write permissions only to specific jobs that require them [6, 26].
You can also integrate OpenSSF Scorecards into your workflows to identify risky practices, such as unpinned actions or overly permissive tokens [6, 26]. Before adopting new actions, review their source code and look for a "Verified creator" badge to ensure their integrity.
Conclusion: Building a Secure and Scalable Code Base with GitHub
Centralizing proprietary code within GitHub offers a single, up-to-date source of truth. This setup, paired with the automation capabilities of GitHub Actions, simplifies deployments, strengthens security, and cuts down on manual tasks. Together, these features create a foundation for smoother operations and a more secure code base.
Branch management ensures teams can work on multiple features or fixes simultaneously without affecting production environments. Tools like GitHub Issues and Project boards make task tracking and documentation more efficient. Meanwhile, automated workflows take care of repetitive tasks like testing, building, and deploying, allowing your team to focus on more strategic efforts.
To further protect your code, GitHub provides granular access controls and protected branches, limiting who can make changes to critical areas. Automated scans help identify leaked secrets or vulnerable dependencies before they become a problem. As GitHub user ZoeStar42 wisely pointed out:
"GitHub’s security is as strong as the practices you employ. Use strong authentication, manage access carefully, and always be mindful of what you’re pushing".
Scalability is another major advantage. For example, GitHub Enterprise accounts allow for centralized policy and billing management across multiple organizations. Reusable workflow templates and shared actions ensure consistent deployment and security practices across all teams, reducing the risk of fragmentation as your organization grows.
To maximize security and efficiency, adopt best practices like enabling two-factor authentication, using private repositories, implementing CODEOWNERS files, and regularly auditing access permissions. By leveraging GitHub’s organizational tools and the automation power of GitHub Actions, you can build a code base that grows securely alongside your business.
FAQs
How does GitHub Actions help secure my code base?
GitHub Actions helps secure your codebase by automating essential workflows and adding important protections. One standout feature is artifact attestations, which confirm software integrity and trace the origin of builds, ensuring your code remains reliable. It also boosts deployment security through OpenID Connect authentication, minimizing risks tied to credential management.
To take security even further, you can adopt best practices like securely managing secrets and applying the principle of least privilege. These tools and strategies make it simpler to address vulnerabilities, stay compliant, and protect your proprietary code.
What are the advantages of using a CODEOWNERS file in GitHub?
A CODEOWNERS file in GitHub is a powerful tool for keeping your codebase organized and well-managed. It allows you to assign ownership of specific files or directories to certain individuals or teams, creating clear lines of accountability. This means that when changes are proposed, the designated owners are automatically notified and asked to review, helping to maintain both code quality and security.
By requiring approvals from the right people before any changes are merged, this process ensures that review standards are consistently upheld. Automating these workflows not only streamlines collaboration but also minimizes the chances of unauthorized changes slipping through. For larger teams or complex projects with many contributors, this feature is especially helpful in keeping everything running smoothly and securely.
What is Dependabot, and how does it help manage dependencies and security updates?
Dependabot is a handy tool designed to help you manage your project dependencies effortlessly while staying ahead of security risks. It scans your codebase for outdated or vulnerable dependencies and then automatically creates pull requests to update them. This proactive approach ensures your projects are patched with the latest security updates and remain protected against potential threats.
By automating these essential tasks, Dependabot not only saves time but also minimizes risks. Your team can focus on building and improving features, knowing that your codebase stays secure and dependable in the background.