QA automation is a game-changer for software development. It saves time, reduces costs, and improves software quality by automating repetitive testing tasks. Instead of relying on manual testers, automation uses tools and scripts to run thousands of tests across devices and browsers in minutes. Here’s what it delivers:
- Faster Testing: Automation cuts testing cycles by 88%, slashing regression testing from weeks to hours.
- Higher Test Coverage: Automated tests handle edge cases and large datasets that manual testing often misses.
- Cost Savings: Fixing bugs early is up to 30x cheaper. Automation also reduces labor costs by up to 50%.
- Scalability: It supports growing projects by running thousands of tests simultaneously.
- Better Bug Detection: 68% of companies using automation find defects earlier, reducing production issues.
Automation integrates seamlessly into DevOps workflows, enabling continuous testing in CI/CD pipelines. It transforms QA from a bottleneck into a driver of faster, more reliable software releases. For IT teams, the question isn’t if they should adopt automation – it’s how soon they can start.
QA Automation: Boost Efficiency and Quality in Your Software Projects!
sbb-itb-05efa2a
Problems with Manual QA Testing
Manual testing presents significant challenges for IT teams, especially when development cycles speed up. Human testers often struggle to keep up with rapid code changes, turning manual QA into a bottleneck. This forces teams to choose between thorough testing and meeting deadlines. In fact, about 47% of software releases are delayed because manual testing simply can’t keep pace.
Slow Testing Processes
Testing manually slows down development timelines, as testers must repeat the same steps for every release. For instance, a typical application with roughly 2,847 test scenarios demands around 89 hours of manual effort per release. Regression testing, which involves re-checking existing features, can stretch what should be quick checks into days-long tasks.
The financial toll is just as concerning. For enterprises, an hour of downtime for a critical application can cost over $300,000. When manual testing drags on for days or weeks, it delays the feedback developers need to refine their code during short Agile sprints.
Incomplete Test Coverage and Human Error
Even the most experienced testers aren’t immune to mistakes. Repetitive tasks can lead to fatigue and distraction, causing missed steps, overlooked bugs, and inconsistent results. Unlike automated testing, which executes the same way every time, manual tests can vary between runs, reducing reliability. Under tight deadlines, teams often prioritize core features, leaving edge cases and complex scenarios unchecked.
The cost of these gaps is immense. Fixing a bug in production is estimated to be 50 times more expensive than addressing it earlier in the process. Poor software quality from missed defects costs the U.S. economy an estimated $2.41 trillion annually.
Difficulty Scaling Testing Efforts
Scaling manual testing is a logistical and financial challenge. It requires hiring more testers, which quickly becomes unsustainable. For larger projects, testing across thousands of browser, device, and operating system combinations is nearly impossible with manual efforts alone. Additionally, manual testers can’t simulate high-load conditions, like thousands of users accessing the system simultaneously, making performance testing impractical without automation.
The economics of manual testing are equally discouraging. At scale, it can result in a negative return, costing more than the issues it aims to prevent. Meanwhile, teams stuck in manual regression cycles risk falling behind competitors who release features faster and gain market share. Automation addresses these scaling issues by running tests quickly and consistently, making it an essential tool for modern QA processes.
How QA Automation Improves Efficiency
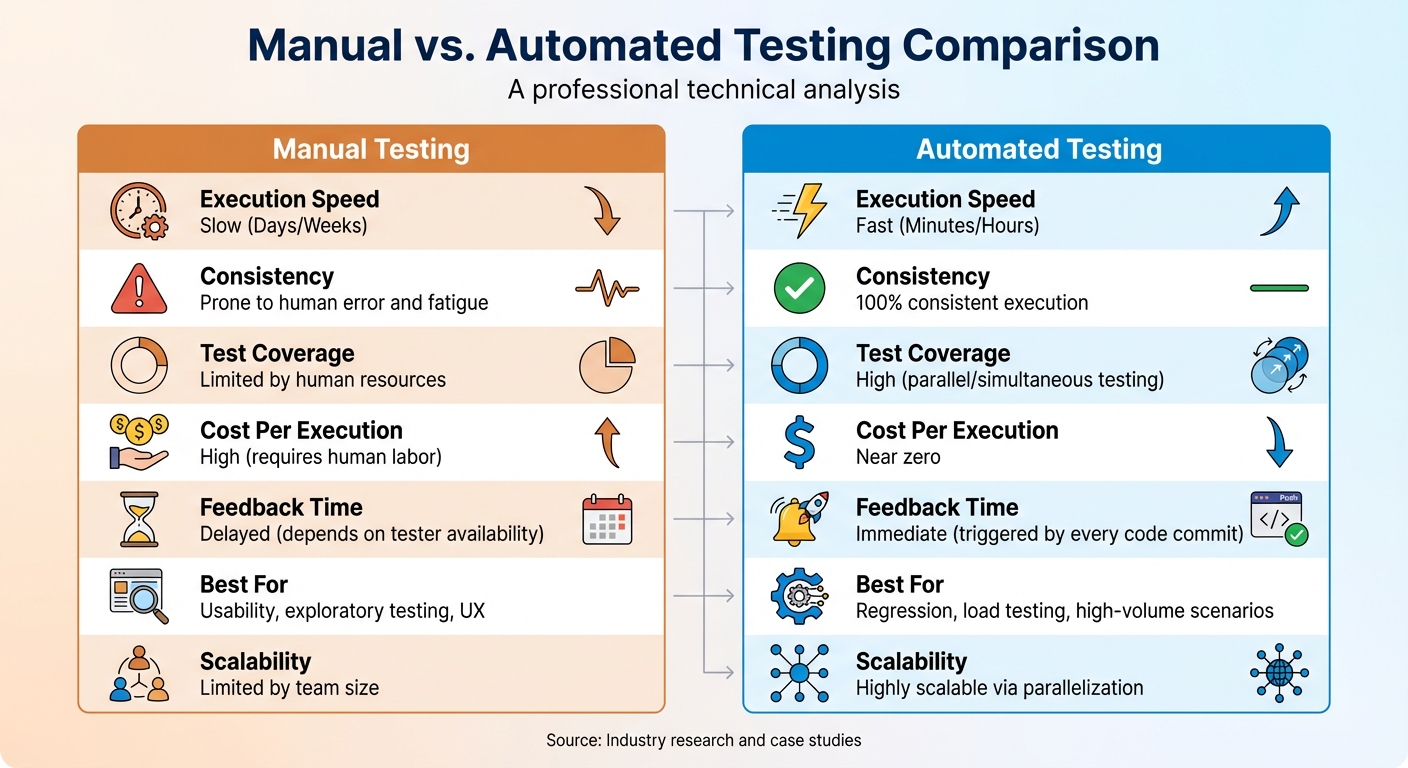
Manual vs Automated QA Testing: Speed, Cost, and Coverage Comparison
QA automation addresses the challenges of manual testing by streamlining workflows and speeding up testing processes. Automated test suites operate continuously, providing results in a fraction of the time it takes manual methods. This rapid feedback loop allows developers to address issues within minutes rather than days, accelerating release cycles and improving software quality overall.
Faster Testing Cycles
Automation dramatically shortens testing timelines. Companies that implement automated testing report a 20% to 40% boost in QA productivity, with testing cycles reduced by 30% and manual effort cut by 40%. Advanced AI-driven tools take this even further, slashing test creation time by up to 90% and speeding up bug fixes by 70%. Regression testing sees some of the most notable improvements – tasks that once required two weeks of manual effort can now be completed in just four hours, cutting testing time by as much as 80%.
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Automation forms the backbone of modern CI/CD pipelines, enabling teams to "build fast, test fast, fail fast". Every code push triggers automated tests – unit, integration, and regression – at each stage of the CI/CD process. This rapid feedback catches defects early, when they are far less costly to fix. Studies show that resolving bugs in production can cost up to 50 times more than addressing them during development. Additionally, parallel testing allows multiple device-browser configurations to be validated simultaneously, eliminating bottlenecks. Instead of sequential testing, automation handles thousands of scenarios at once. It’s no surprise that 76% of organizations view test automation as essential for faster releases, and 46% have automated more than half of their testing.
Manual vs. Automated Testing Comparison
| Feature | Manual Testing | Automated Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Speed | Slow (Days/Weeks) | Fast (Minutes/Hours) |
| Consistency | Prone to human error and fatigue | 100% consistent execution |
| Test Coverage | Limited by human resources | High (parallel/simultaneous testing) |
| Cost Per Execution | High (requires human labor) | Near zero |
| Feedback Time | Delayed (depends on tester availability) | Immediate (triggered by every code commit) |
| Best For | Usability, exploratory testing, UX | Regression, load testing, high-volume scenarios |
| Scalability | Limited by team size | Highly scalable via parallelization |
Cost Savings from QA Automation
When it comes to QA automation, the financial benefits are hard to ignore. While the upfront costs of setup may seem steep, automation quickly pays for itself, delivering ongoing savings that grow with each test cycle. Let’s explore how automation reduces costs, starting with labor savings and moving into defect reduction and ROI from repeated test execution.
Reduced Labor Costs Over Time
One of the most immediate financial advantages of automation is the reduction in labor costs. Unlike manual testing, which scales directly with the number of tests, automation allows you to handle larger workloads with fewer people. For instance, a manual testing team managing 500 tests might need 12 engineers, costing around $900,000 annually. In comparison, an automation team can handle the same workload with just five engineers, costing about $500,000 – cutting payroll expenses by nearly 50%.
Automation also operates beyond the limitations of an 8-hour workday. Automated tests can run 18–24 hours a day without incurring overtime costs, unlike manual testers. As Martin Schneider, Delivery Manager at BrowserStack, highlighted:
"Before BrowserStack, it took eight test engineers a whole day to test. Now it takes an hour. We can release daily if we wanted to." [28,5]
Although the initial setup costs for automation are higher, the cost per test execution drops significantly after the first few regression cycles. For example, while ROI in the first year may hover around 57.5%, it can soar to over 186% in subsequent years as setup costs are amortized.
Lower Defect Costs
Fixing defects early is much cheaper than addressing them after deployment. A defect caught during development might cost just $89 to resolve, while the same issue in production could cost $4,467 – up to 100 times more [4,30]. Worse, a single customer-facing defect could lead to a financial hit of around $67,890.
Automation makes it easier to adopt shift-left testing, catching issues earlier in the development cycle. By identifying defects at the code-commit stage, organizations can prevent costly problems from reaching production. This approach not only saves money but also reduces defect leakage to production by 30% to 50%. Companies leveraging data-driven QA strategies report a 30% reduction in overall software defects.
"The cost isn’t in fixing bugs. It’s in the opportunities lost while fixing bugs." – Rishabh Kumar, Marketing Lead, Virtuoso QA
By lowering defect costs, automation significantly enhances the financial return on investment.
ROI from Repeated Test Execution
The financial benefits of automation grow with every test run. Consider this: a single automated test performed daily can save over 480 hours of manual labor annually. Once the automation framework is in place, the cost of each subsequent test execution is minimal compared to the ongoing expenses of manual testing.
Most organizations see their break-even point within 6 to 12 months of implementing automation. For example, in Year 1, automation might cost $29,000 while saving $33,644 in manual testing expenses, resulting in a 16% ROI. By Year 2, with a $14,000 maintenance investment, savings could climb to $55,264 – an impressive 395% annual ROI.
To maximize returns, automation efforts should focus on the critical 20% of test cases – such as regression, smoke, and high-risk scenarios – that typically uncover 80% of major issues. This strategic approach ensures that the financial and operational benefits of automation are fully realized.
Better Software Quality and Reliability
Beyond improving efficiency and cutting costs, QA automation plays a key role in enhancing software quality. It doesn’t just speed up testing – it ensures products are more reliable by subjecting them to thorough, consistent, and repeatable testing processes.
More Complete Test Coverage
Manual testing has its limits. Even the most experienced QA team can only cover so much ground before deadlines loom. Automation, however, eliminates these constraints. Automated scripts can execute thousands of tests across a wide range of scenarios, including rare edge cases – like unusual input combinations or specific business logic paths – that manual testers might miss due to time pressure or fatigue.
One standout feature of automation is its ability to handle data-driven testing. This approach allows a single test scenario to run with thousands of different data sets, often pulled from XML, JSON, or CSV files. It’s an efficient way to validate how an application performs with a broad array of inputs, without the errors or monotony that often accompany manual testing. For tasks like load testing, where simulating thousands of concurrent users is necessary, automation becomes indispensable.
Consistent and Reliable Results
Human testers have limits – they can get tired, distracted, or accidentally skip steps. Automation removes these human variables. As Dennis Martinez, a freelance automation tester and DevOps engineer, puts it:
"Automation will handle those repetitious tasks the same way every time you execute them, increasing the consistency and reliability of each test run."
This level of consistency is especially valuable for agile teams working in short sprints. Reliable, repeatable tests provide developers with faster feedback, helping to cut testing cycles by as much as 88%. Consistency not only minimizes errors but also makes it easier to catch defects early, which is crucial in agile workflows.
Earlier Bug Detection
Catching bugs early is always cheaper than fixing them later, and automation is designed to do just that. When integrated into CI/CD pipelines, automated tests detect defects right away, significantly reducing the cost of fixes and the risks associated with delayed discovery. This "shift-left" approach ensures bugs are identified during the early stages of development, long before they can cause issues in production.
The benefits are clear: 68% of companies that automated at least half of their testing reported finding bugs earlier in the development process. This not only keeps costs under control but also helps avoid software failures that could alienate users.
Automation also strengthens the depth and scope of testing, ensuring new features work without breaking existing functionality. As BrowserStack aptly states:
"Automation testing increases the depth and scope of the tests to improve the software quality."
Scalability and Cybersecurity Benefits
As software projects become more complex, QA automation steps in as a critical tool for managing growth and safeguarding against security risks. For teams dealing with microservices, distributed systems, or fast-paced deployment schedules, automation is no longer optional – it’s essential. Let’s take a closer look at how automation handles the challenges of scaling and enhances cybersecurity in large-scale projects.
Scaling QA for Larger Projects
The true strength of automation becomes clear as projects grow. With parallel execution, tests can be distributed across multiple cloud-based nodes, enabling thousands of scenarios to run at the same time. This reduces testing time from what used to take days or weeks to just minutes or hours. Cloud infrastructure eliminates the need for physical device labs, offering instant access to a wide range of real device and browser combinations without the hassle of managing hardware.
Additionally, smart frameworks use test impact analysis to pinpoint which tests are impacted by specific code changes. This ensures only the relevant scripts are run, saving time and resources. For instance, a fintech startup revamped its testing process by adopting cloud-based parallel execution. This shift cut their total test suite execution time from eight hours to just 90 minutes, all while improving their ability to catch defects.
Improved Cybersecurity
Automation also strengthens security by identifying vulnerabilities before they make it to production. Integrated with CI/CD pipelines, automated tools scan every build for risks like SQL injection and hard-coded credentials. Considering that cybercrime could cost $10.5 trillion annually by 2025 and that the average cost of a security breach is $4.88 million, proactive security measures are more important than ever.
Automated tools can scan thousands of endpoints, APIs, and configurations simultaneously, ensuring that any threats are detected early. They also create a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM), which tracks third-party components and open-source libraries to flag known vulnerabilities in the supply chain. For industries with strict regulations, automated checks ensure compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS by verifying secure code paths and authentication protocols. By seamlessly embedding security into the QA process, automation not only protects software but also boosts its reliability.
A remarkable example comes from Airbus Intelligence, which in December 2024 integrated automated security scans into its CI/CD pipeline. This change reduced release times from 24 hours to just 10 minutes. Software Automation Engineer Logan Weber explained:
"What used to happen is we would touch one part of the code and it would break another part. Now, each time a developer pushes code, we can immediately identify problems."
Impact on Deployment Frequency and Defect Rates
The benefits of automation extend beyond testing to deployment practices and overall software quality. The metrics speak for themselves:
| Metric | Before QA Automation | After QA Automation Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Release Frequency | Monthly or Bi-weekly | Daily or On-demand |
| Regression Cycle Time | Days or Weeks | Minutes or Hours |
| Defect Leakage to Production | High (approx. 34 bugs/month) | Low (approx. 3 bugs/month) |
| Maintenance Effort | High (60% of QA time) | Low (5% with AI/Self-healing) |
| Test Coverage | Limited/Manual | Comprehensive (Cross-browser/device) |
| Cost to Fix Bugs | 30x higher (Production) | Baseline (Development) |
The real-world advantages of automation are undeniable. Take Shopify during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, for example. By leveraging automated quality processes, the company scaled its platform to handle a massive surge in traffic and transactions. This effort helped Shopify process an additional $120 billion in merchant sales, turning what could have been a crisis into a moment of extraordinary growth. With automation, scaling confidently becomes not just possible but transformative.
Conclusion
QA automation is more than just a tool – it’s an investment that delivers measurable returns. As highlighted earlier, it speeds up testing cycles, cuts costs, and boosts overall software quality. Companies automating at least half of their tests report 88% shorter testing cycles, 71% improved test coverage, and 68% earlier bug detection during development. Many organizations see a full return on investment within just 6 to 12 months.
One of the standout advantages is cost efficiency. Automation helps manage growing product complexity without inflating manual testing costs. A small, focused team can handle larger workloads, potentially cutting payroll expenses by up to 50% as projects scale. For instance, a manual team managing 500 tests might need 12 people, costing around $900,000 annually. Meanwhile, an automation-driven team achieves the same results with just five people, costing $500,000 per year. Beyond these savings, addressing defects early in development is far cheaper than fixing them post-release, where costs can balloon to 30 times higher.
But the benefits don’t stop at efficiency and cost-cutting. Automation transforms team dynamics by freeing QA professionals from repetitive tasks. This shift allows teams to focus on innovation and optimizing performance, enabling the rapid release cycles modern businesses demand. Instead of being a bottleneck, quality assurance becomes a competitive edge. As Aparna Ramesh, Senior Executive at Aspire Systems, explains:
"The real business value of test automation lies in its power to turn quality assurance into a catalyst for assured business success."
For IT leaders tackling complex software challenges, the question isn’t whether to adopt automation but how quickly to get started. Begin with high-value, repetitive regression tests to demonstrate ROI, then scale thoughtfully. Encourage teams to prioritize innovation over routine checks, treat test code with the same care as production code, and integrate automation into CI/CD pipelines. By focusing on metrics that resonate with leadership, businesses can drive faster releases while ensuring sustainable growth and robust security. The companies thriving today aren’t just building software faster – they’re building it smarter, with automation as the cornerstone.
FAQs
Which tests should we automate first?
Start by focusing on tests that are repetitive, stable, and essential to your core business operations. High-priority candidates include high-volume, time-consuming, and error-prone tests, such as regression tests for critical features. Begin automating unit and integration tests first – they’re simpler to maintain and provide quicker results. Once those are in place, you can move on to more complex end-to-end tests. This method not only speeds up feedback but also cuts down on manual work while boosting overall software quality.
How long does it take for QA automation to pay off?
QA automation often recoups its costs within 6 to 12 months, depending on factors like the scope of implementation and the specific project environment. This timeline highlights the benefits automation brings, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and fewer errors.
How do automated tests fit into a CI/CD pipeline?
Automated tests play a key role in any CI/CD pipeline, making it easier to validate code changes with speed and consistency. These tests run automatically as part of the pipeline, helping to simplify the processes of building, testing, and deploying software. By incorporating various types of tests – such as unit, integration, and performance testing – teams can identify regressions early, enhance code quality, and push updates faster. While prioritized tests offer quick feedback, more comprehensive tests can run asynchronously, enabling scalable and dependable deployment workflows.