When you think of release processes, you might picture developers deploying code. But here’s the truth: releases impact every department, not just IT. Whether it’s rolling out a new payroll system in HR, updating cybersecurity protocols, or launching a marketing campaign, structured release processes can save time, reduce errors, and improve coordination across teams.
Key takeaways:
- 68% fewer deployment failures occur with structured release practices.
- Teams with clear workflows and documentation are twice as likely to hit business goals.
- Poorly managed changes cause 75% of service issues.
A proper release process ensures smooth transitions, minimizes risks, and aligns teams like IT, HR, Marketing, and Security. It’s about turning complex updates into predictable, manageable tasks. Let’s break it down.
Release Management: Best Practices and Strategies
sbb-itb-05efa2a
What Release Management Means for Your Entire Business
Ad-Hoc vs Structured Release Processes: Key Differences and Benefits
Release management isn’t just about moving code; it’s about orchestrating a seamless process across development, testing, and deployment to ensure changes are delivered safely and efficiently. Think of it as air traffic control, turning what could be chaotic, high-stakes events into smooth, predictable workflows.
The real game-changer? Release management extends beyond IT. It involves coordinating efforts across departments like Marketing, Sales, and HR. Whether it’s rolling out a new HR system or implementing cybersecurity updates, every department benefits from a structured release process.
The business world is shifting from a project-based approach – where work ends at delivery – to a product-based approach that focuses on continuous updates and long-term support. Release management, therefore, becomes an ongoing effort. Gabriel Gutierrez from Boeing sums it up well:
"Companies must provide a common forum where changes are fully vetted and put through thorough architectural and design reviews that eventually lead to integrated testing. Cross-functional and technical reviews are essential to minimizing the inevitable pain after go-live".
How Release Processes Work in Different Departments
The core principles of release management – planning, testing, and controlled deployment – adapt to fit the needs of different teams. Here’s how it works:
- IT Operations ensures infrastructure is ready, environments are consistent, and system health is closely monitored during rollouts.
- HR Systems focus on timing releases with employee communications, managing access controls, and ensuring payroll or benefits systems remain uninterrupted.
- Cybersecurity incorporates compliance checks and dependency scanning directly into the pipeline to catch vulnerabilities early.
No matter the department, the mechanics remain the same: staging environments for testing, quality gates to verify readiness, and clear communication to keep everyone informed. This consistency highlights the difference between chaotic ad-hoc releases and well-structured processes.
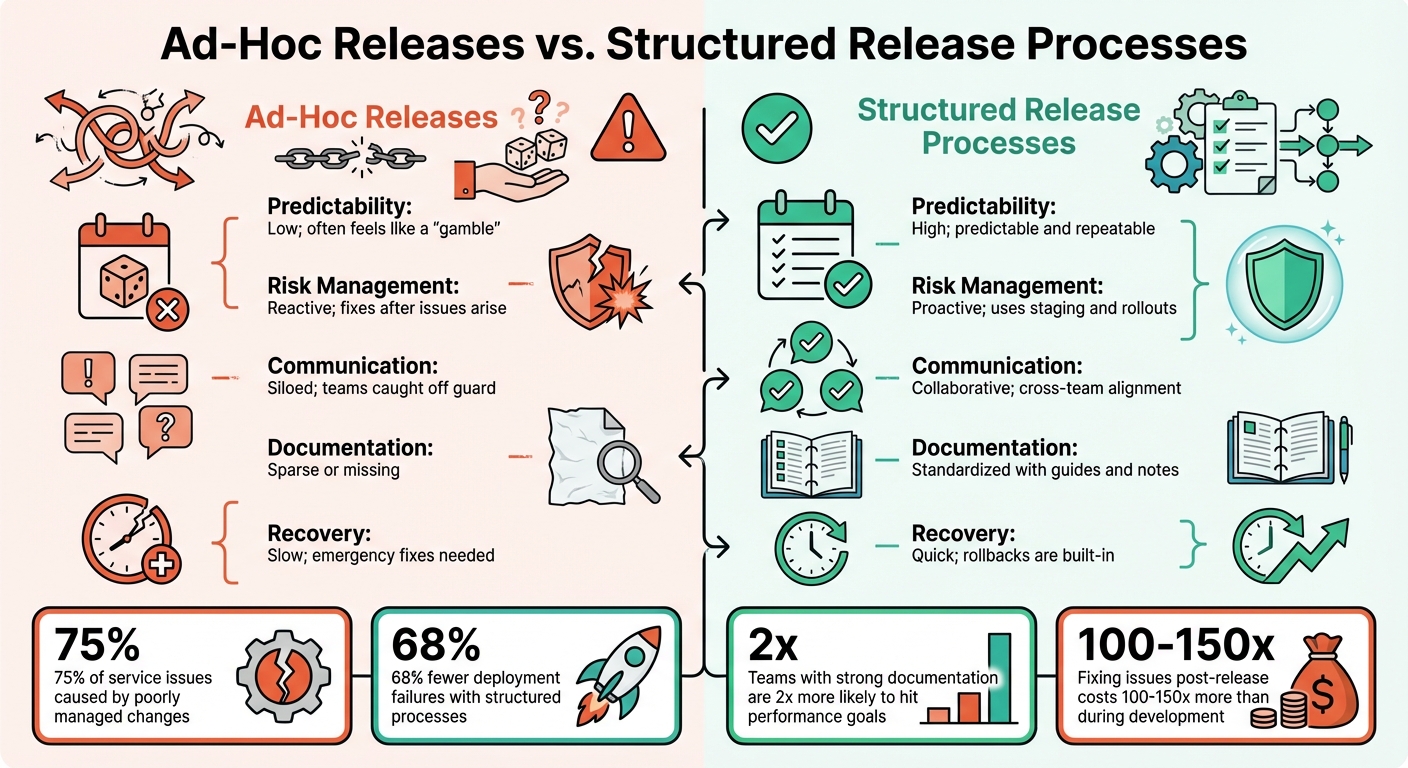
Ad-Hoc Releases vs. Structured Release Processes
The difference between unstructured and structured releases couldn’t be more pronounced. Ad-hoc releases are often reactive and disorganized, with teams "throwing changes over the wall" without proper coordination. This approach leads to missed dependencies, failed deployments, and late-night emergencies that drain team morale. For example, sales teams might be blindsided by feature changes during customer demos, or support staff may struggle to answer user questions because they weren’t briefed on updates.
On the other hand, structured release processes eliminate these headaches. They create predictable workflows that reduce deployment failures by 68% over the last decade. Teams with strong documentation are twice as likely to hit their performance goals. Plus, fixing issues post-release can cost 100–150 times more than addressing them during development or testing.
| Feature | Ad-Hoc Releases | Structured Release Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Predictability | Low; often feels like a "gamble" | High; predictable and repeatable |
| Risk Management | Reactive; fixes after issues arise | Proactive; uses staging and rollouts |
| Communication | Siloed; teams caught off guard | Collaborative; cross-team alignment |
| Documentation | Sparse or missing | Standardized with guides and notes |
| Recovery | Slow; emergency fixes needed | Quick; rollbacks are built-in |
Structured processes rely on tools like staging environments, quality gates, and progressive delivery techniques (e.g., canary releases) to identify and fix issues before they impact users. This turns releases from risky, stressful events into routine, manageable tasks that teams can handle with confidence.
Why Release Processes Matter Outside of Development
Structured release processes aren’t just for development teams – they bring order and efficiency to the entire organization. By standardizing how updates are planned and executed, businesses can streamline operations and improve coordination across departments.
Better Efficiency and Productivity
Standardized release processes save time and boost productivity across the board. Instead of reinventing the wheel for every update, teams can rely on pre-approved workflows and templates. For example, HR rolling out a new benefits platform or IT Operations patching a server can follow a clear, repeatable process, reducing manual effort. In fact, up to 70% of low-risk, repetitive tasks can be automated, freeing employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
The cost savings are just as striking. Resolving live issues is 100–150 times more expensive than fixing problems during testing. Teams that maintain high-quality documentation are also more than twice as likely to hit their performance targets. A shared release calendar further enhances efficiency by helping departments like Marketing and HR avoid scheduling conflicts during critical periods, such as retail holidays or year-end financial reporting.
Lower Risk and Fewer Errors
Structured processes act like safety nets, ensuring that updates are thoroughly tested and validated before going live. This approach has led high-performing teams to achieve release success rates of 90% or higher.
Without these processes, chaos often ensues. Systems can turn into "unique snowflakes" – manually configured environments that are difficult to replicate. This leads to the infamous "works on my machine" dilemma, where testing conditions don’t match production environments. Automation mitigates these risks by guaranteeing that every step, from compliance checks to permission updates, is executed consistently. As the Google SRE Book wisely notes:
"It’s cheaper to put good practices and process in place early, rather than have to retrofit your system later".
These safeguards not only reduce errors but also smooth collaboration across departments.
Better Team Communication and Alignment
A structured release process fosters better communication and alignment across teams. By creating a unified framework, departments like Sales, Support, and HR stay informed and on the same page. This transparency eliminates the "thrown over the wall" mentality, where teams only learn about changes after they’ve caused problems.
The stakes are high. In 2022, poor software quality cost the U.S. economy approximately $2.41 trillion, and one in three customers abandoned a brand after just one bad experience. Jesse Sumrak from LaunchDarkly sums it up perfectly:
"Release management is the bridge that connects your development efforts to the end-user experience".
How to Build a Release Process for Your Organization
Creating a release process doesn’t mean you have to reinvent the wheel. Start by assessing your current setup, then add structure where it’s truly needed. The aim is to minimize chaos while avoiding unnecessary red tape. Here’s how you can evaluate your existing workflows, establish clear procedures, and define responsibilities to create a streamlined release process.
Review Your Current Workflows and Identify Gaps
Start by mapping out your release process from start to finish – everything from the initial request to deployment. Include details like roles, tools, and handoffs along the way. Look for pain points where delays or errors are common. Retrospectives on recent releases can help reveal recurring issues, such as bottlenecks or quality concerns. Also, check if your staging environment mirrors production and ensure you have a documented rollback plan in place.
Automation can be a game-changer here. Repetitive manual tasks, like regression testing or building releases, can lead to human error. For example, Amazon automates these processes, enabling them to perform over 50 million code deployments annually – more than one every second. Additionally, evaluate your communication channels. If teams only find out about updates during customer demos, there’s clearly a gap. This review ensures your process aligns with broader business goals.
Create Standard Procedures
Once you’ve pinpointed the gaps, it’s time to formalize your process. Develop clear, repeatable workflows for each stage of the release cycle. This reduces confusion and keeps things running smoothly. Begin with a strategy review to confirm that each release aligns with your company’s objectives.
Use a standard template to define expectations for each major release. This should outline when teams like Marketing, Sales, and Support need to step in and what they’re responsible for. As Tony Kelly from Octopus Deploy puts it:
"Standardized release processes ensure consistency, predictability, and efficiency… Organizations can minimize errors by defining clear workflows, checklists, and procedures".
Incorporate quality gates – checkpoints that must be cleared before moving to the next stage, whether it’s from development to staging or staging to production. Feature flags are another helpful tool, allowing you to separate the technical act of deployment from the decision to release, making live testing safer. Lastly, establish measurable KPIs and service-level agreements to track the success of each release.
With procedures in place, the next step is to ensure your teams are equipped to execute them effectively.
Train Your Teams and Define Responsibilities
Clear ownership eliminates confusion. Define key roles early, such as a Release Manager to oversee coordination, a Product Owner for requirements, a Quality Manager to handle acceptance criteria, and a DevOps team to maintain infrastructure stability. Training shouldn’t stop with technical teams. Departments like Sales, Marketing, Customer Support, and Legal also need to understand how releases impact their work.
Jen Dunbeck, Release Manager at BitTitan, emphasizes the importance of internal communication:
"If you don’t have a way to communicate the change internally, your salespeople will be surprised when showing customers demos that have feature or button changes".
To promote alignment across teams, establish regular communication routines and use consistent channels to share updates. After each release, conduct retrospectives to refine training and adjust roles as needed. Considering that around 45% of developed features go unused by customers, focusing training on delivering value is essential.
Release Processes in Different Business Areas
Release processes go beyond software updates. They play a crucial role in IT operations, HR systems, and cybersecurity, where unplanned changes can disrupt entire organizations. Let’s explore how structured release strategies are applied across these vital areas.
IT Operations
IT operations oversee everything from server updates to infrastructure changes, and structured release processes keep these activities running efficiently. Automation is key – consistent, reliable services depend on automated procedures for building binaries and configurations, ensuring uniformity across systems. For instance, Amazon handles over 50 million deployments annually.
One effective risk management approach is canarying – rolling out updates to a small group of users first (the "canary") to assess performance before a full deployment. This reduces the risk of widespread issues, as most IT incidents arise from binary or configuration changes rather than hardware failures.
Another valuable tool is feature flags, which allow teams to deploy code to production without immediately activating it for users. This eliminates the need for maintenance windows and provides the flexibility to deactivate features instantly if problems occur. High-performing IT teams also embrace self-service models, enabling teams to manage deployments with minimal manual intervention.
HR Systems
HR systems, like payroll or benefits platforms, require structured release processes to avoid disrupting business operations. Timing matters – updates should align with business calendars to steer clear of critical periods like tax year-end or open enrollment.
A Change Advisory Board (CAB) is essential for assessing the impact of updates on employee data and overall stability. As Jen Dunbeck, Release Manager at BitTitan, explains:
"A key function of [a change control board] is to help the organization assess risk and impact with impartiality. They also help root out technical dependencies that may not have been evident".
Testing updates in staging environments that replicate production systems is critical. This ensures issues, such as payroll calculation errors, are caught before they affect employees. Progressive rollout techniques, including canary releases and feature flags, further reduce the risk of system-wide failures. Collaboration across HR, IT, and Finance ensures dependencies, like single sign-on access, are fully addressed.
Cybersecurity Implementations
Cybersecurity updates, such as patches and compliance changes, require speed and precision to protect systems without compromising agility. A structured release process ensures these updates are deployed securely and on time. Integrating security into the release pipeline – a practice known as DevSecOps – enables early detection of vulnerabilities through dependency scanning and security testing during the build phase, saving time and resources compared to fixing issues in production.
Automated pipelines and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) help maintain consistent security configurations and allow for immediate rollbacks when necessary. Security releases should also respect blackout periods, such as major retail holidays, to maintain stability during critical times. Quality gates enforce security checks before production, while automated audit trails ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Tools and Automation for Release Processes
Automation takes the guesswork out of software releases, reducing manual errors and streamlining workflows. With the right tools, teams can move changes through testing, approval, and deployment stages efficiently and consistently. As Stephen Watts from Splunk succinctly puts it:
"The #1 rule in DevOps? Automate anything that can improve the efficiency of your people, processes and technology".
CI/CD pipelines like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and AWS CodePipeline ensure that code progresses seamlessly through build and test stages, keeping it ready for release. Deployment tools such as AWS CodeDeploy and Octopus Deploy handle the technical aspects of rolling out changes across servers, minimizing the chance of human error during production updates. Meanwhile, Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform and Ansible make it possible to replicate production environments locally, ensuring consistency across all stages of development.
Feature management platforms, including LaunchDarkly and Statsig, allow teams to separate deployment from release. This means code can be shipped without activating new features immediately. Teams can roll out updates gradually to specific user groups and quickly disable features if issues arise, thanks to built-in "kill-switches". These tools not only reduce risk but also improve deployment stability, setting the stage for robust testing processes.
Automated Testing and Deployment
Automated testing is a critical safety net, catching bugs before they reach users. Fixing issues during development is far more cost-effective – resolving bugs in production can cost 100–150 times more. Automated unit, integration, and acceptance tests validate changes in staging environments that mirror production, ensuring updates to systems like HR tools or IT infrastructure work as intended.
High-risk tasks should be the first to be automated. While it might seem logical to keep humans involved in complex tasks, automation shines in areas where errors could have serious consequences. Elite development teams integrate code multiple times daily, relying on automated checks to ensure that the main code branch remains error-free. In cybersecurity, DevSecOps practices integrate security scans into the CI/CD pipeline, catching vulnerabilities during the build phase rather than post-deployment.
Automated rollbacks add an extra layer of protection. If monitoring tools detect anomalies after deployment, systems can automatically revert to a stable state, ensuring uptime for critical operations like payroll or network infrastructure. Staged rollouts, such as canary releases or blue-green deployments, allow teams to expose updates to a small user group first, addressing potential issues before a full launch. Once releases pass automated tests and rollouts, monitoring tools track their real-time performance, ensuring smooth operations.
Monitoring and Tracking Tools
Real-time monitoring tools like Splunk, PagerDuty, and Datadog provide invaluable insights into system performance, sending alerts when key metrics deviate from expected thresholds. This "early life support" phase right after a release is crucial for identifying and resolving issues before they escalate.
Effective monitoring goes beyond internal system checks, covering end-to-end service behavior to catch subtle problems that might otherwise slip through. Aligning metrics with Service Level Indicators (SLIs) and Service Level Objectives (SLOs) ensures that measurements reflect real user experiences. A well-executed release process should aim for a success rate of 90% or higher.
Teams that track DORA metrics – such as deployment frequency, lead time for changes, Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR), and change success rate – can identify areas for improvement and drive better outcomes. Automated audit trails generated by these tools are critical for meeting compliance requirements in regulated industries like finance and healthcare. Integration with platforms like Slack ensures that real-time updates about release phases and any regressions are shared with stakeholders. Additionally, teams with strong documentation and monitoring practices are more than twice as likely to meet or exceed their performance goals.
Conclusion
Release management has evolved far beyond being just a developer’s concern – it’s now a strategic framework that ensures seamless transitions from planning to production across an organization. This holistic approach not only enhances technical results but also contributes to broader business success. Whether you’re launching a new HR platform, upgrading cybersecurity measures, or implementing IT infrastructure changes, a structured release process protects revenue and cuts deployment failures by as much as 68%. It also ensures that teams in Sales, Marketing, Support, and Operations are ready to handle upcoming updates.
The numbers speak volumes: roughly 75% of digital service issues are tied to poorly managed changes.
To address this, effective release management hinges on collaboration. A unified review process – bringing together IT, Finance, Legal, and other departments – enables thorough vetting of changes. Gabriel Gutierrez from Boeing highlights the importance of this approach:
"Cross-functional and technical reviews are essential to minimizing the inevitable pain after go-live".
This level of coordination transforms release management into a strategic tool that aligns every department with shared organizational objectives.
To strengthen your release process, focus on standardizing workflows, automating repetitive tasks, and establishing clear ownership. Techniques like feature flags can separate deployment from release, shared calendars can improve visibility, and tracking metrics such as deployment frequency and mean time to recovery can help measure success. Research shows that organizations with strong documentation and structured processes are over twice as likely to achieve their performance goals.
A well-executed release process brings together design, development, testing, and deployment, creating a system that turns change into a driver of efficiency and growth.
FAQs
How can teams outside of IT benefit from having a structured release process?
A well-organized release process can make a big difference for non-IT teams like HR, cybersecurity, and operations. By systematically planning updates or changes, these teams can streamline their workflows, cut down on errors, and promote better teamwork. Whether it’s introducing new policies, implementing tools, or deploying security measures, this structured approach helps ensure smoother transitions and fewer disruptions.
It also fosters stronger communication and alignment across different departments, so everyone stays informed and prepared for upcoming changes. With a clear framework in place, teams are better equipped to deliver consistent results and respond effectively to new challenges, enhancing overall efficiency and performance.
What’s the difference between an ad-hoc release process and a structured one?
The key distinction between an ad-hoc release process and a structured release process boils down to how organized and dependable they are. Ad-hoc processes are typically informal and reactive, often lacking a consistent framework. This approach can result in errors, miscommunication, and difficulties in managing teams or dependencies effectively.
In contrast, a structured release process is meticulously planned and follows a set of well-defined procedures. This approach promotes consistency, reduces risks, and ensures that releases align with broader business objectives. It also strengthens team collaboration, minimizes mistakes, and boosts efficiency – especially in projects involving multiple departments or complex workflows.
While ad-hoc processes might seem quicker in the short term, structured processes deliver the reliability and coordination necessary for sustained success across all facets of a business.
Why is automation important for managing release processes across different departments?
Automation plays a key role in managing release processes across departments by cutting down on human error, ensuring uniformity, and simplifying workflows. When repetitive tasks are automated, teams can shift their energy toward more strategic goals, reducing the chances of delays or unexpected hiccups.
Another advantage of automation is its ability to support comprehensive pre-deployment testing. This helps spot and fix potential problems early, preventing them from affecting operations. The result? Smoother rollouts and better teamwork between departments like IT, HR, and cybersecurity.